Tender management is a systematic process that oversees the entire lifecycle of developing, submitting, and evaluating bids for competitive procurement initiatives. It ensures accountability by aligning buyers and suppliers with agreed-upon standards and schedules, fostering a level playing field that promotes transparency and fairness. For procurement professionals, effective tender management is indispensable in identifying cost-effective solutions, maintaining regulatory compliance, and building strong supplier relationships.
By streamlining once labor-intensive and mistake-prone processes with organized systems and advanced technology, organizations can transform tender management into a more efficient and effective practice. This involves a comprehensive approach to handling requests for proposals (RFPs) and comparing supplier proposals, enabling a data-driven decision-making process that drives efficiency and sustainable growth.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of tender management, exploring best practices, technology integration, and strategies for optimizing the tender lifecycle from preparation to award.
What is Tender Management?
Tender management is the formalized tendering process of inviting, evaluating, and ultimately accepting a bid or proposal. It helps organizations deliver better pricing and quality in accordance with the needs of each individual project.
By streamlining the tender management process, companies can win more tenders, win them faster, and stay a step ahead of the competition in today’s rapid-fire global economy. This process addresses and improves on inefficiencies in procurement activities while maximizing achievement of strategic goals through targeted resource investment.
Tender management specifically differs from larger procurement or bidding processes. At its core, procurement is the process of obtaining goods or services. Bidding is simply submitting bids or offers, while tender management is a more robust process that manages the entire lifecycle of a tender from solicitation through awarded contract.
A more organized approach allows organizations to avoid risks such as cost overruns and project delays, keeping projects on their intended schedule. With the right tender management system in place, efficiency improvements can be dramatic.
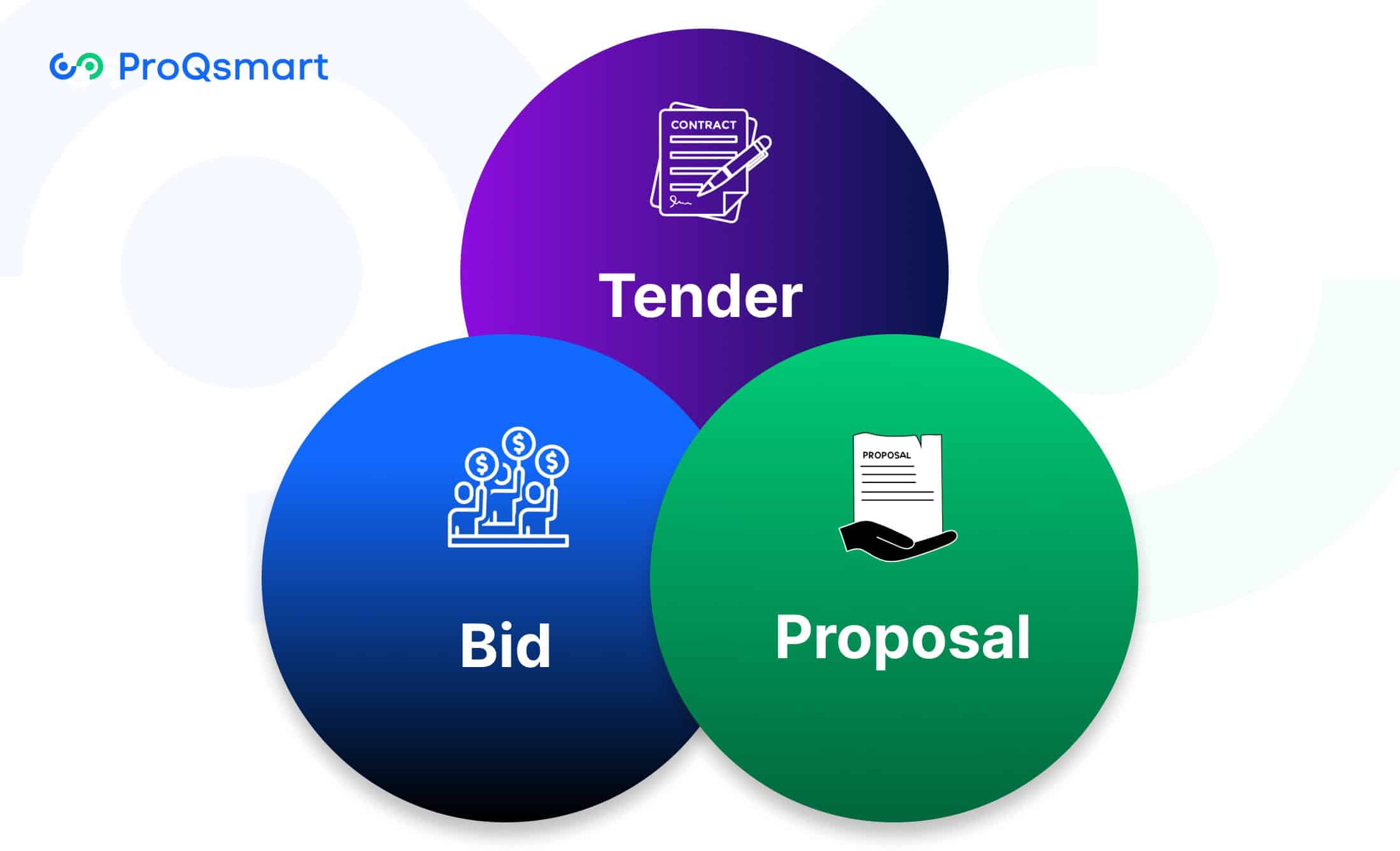
Differences Between Tender, Bid, and Proposal
|
Component |
Definition |
Purpose |
Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Tender |
A formal request for bids on a project or contract. |
To solicit competitive offers. |
Detailed, standardized, and comprehensive. |
|
Bid |
An offer submitted in response to a tender. |
To propose pricing and terms. |
Focused on cost and deliverables. |
|
Proposal |
A document outlining a solution or approach. |
To address specific needs. |
Often creative and tailored. |
Tenders establish the parameters, bids deliver the competitive advantage, proposals bring the strategic mind. A big misconception is that these terms are the same thing. Each one plays a different and important role in the procurement process.
Importance in Procurement Processes
Good tender management encourages transparency, which helps build trust between stakeholders. It promotes competition by bringing in numerous suppliers, creating cost savings through competition and guaranteeing high-quality services.
For instance, about one-third of firms realize quantifiable savings from formalized tender management. Compliance with regulatory frameworks is especially important in the realm of public procurement. Public entities must be diligent to operate transparently and with accountability.
Strategic sourcing initiatives are positively impacted as tender management identifies the best-value suppliers while supporting the alignment of procurement with organizational goals.
With e-tenders, automated workflows, and real-time supplier performance tracking, ProQsmart’s AI-powered platform makes tender management easy. Budget compliance management and subcontractor management tools are integrated into ProQsmart’s tender management system.
This encourages transparency and allows for meaningful cost savings, making it a crucial tool for today’s procurement.
Key Participants in Tendering
Effective tender management relies on the collaboration of multiple key participants, each bringing specialized knowledge and roles to the table. As procurement professionals deepen their understanding of the roles played and collaboration needed, they can better streamline processes and reach desired outcomes efficiently.
Stakeholders Involved in Tendering
These are known as key participants in tendering and they include clients, contractors, consultants, suppliers and regulatory authorities. Clients are the ones who outline the goals and budget of a project, and contractors/suppliers supply the goods or services needed.
Consultants have the ability to provide independent technical or strategic guidance. Each group brings distinct priorities. While clients are primarily concerned with cost and quality, contractors are concerned with feasibility and profitability.
Consultants want to make sure stuff is done right and efficiently. Actively involving all parties fosters trust and aligns goals. For example, candid conversations in procurement can save months.
Miscommunication can derail projects. Using tools like ProQsmart for real-time collaboration ensures consistent updates and document accessibility, minimizing errors.
Roles and Responsibilities in the Process
Tender managers oversee the process, while bid teams prepare submissions. Project managers keep the work flowing between these stakeholders. Tender managers ensure deadlines are met.
Bid teams line up careful document quality control and project managers set out clear communication channels and workflows. Tools such as ProQsmart automate time-consuming processes, from bill of quantities to supplier performance monitoring.
Ownership drives quality. When roles are well defined, accountability helps make sure quality standards are maintained. Assigning tasks based on expertise enhances efficiency, saving costs and resources, especially when supported by ProQsmart’s AI-driven automation.
"Tired of Tendering Hassles? Simplify Your Process with Our Expert Checklist - Download Now!"
Stages of the Tender Management Process
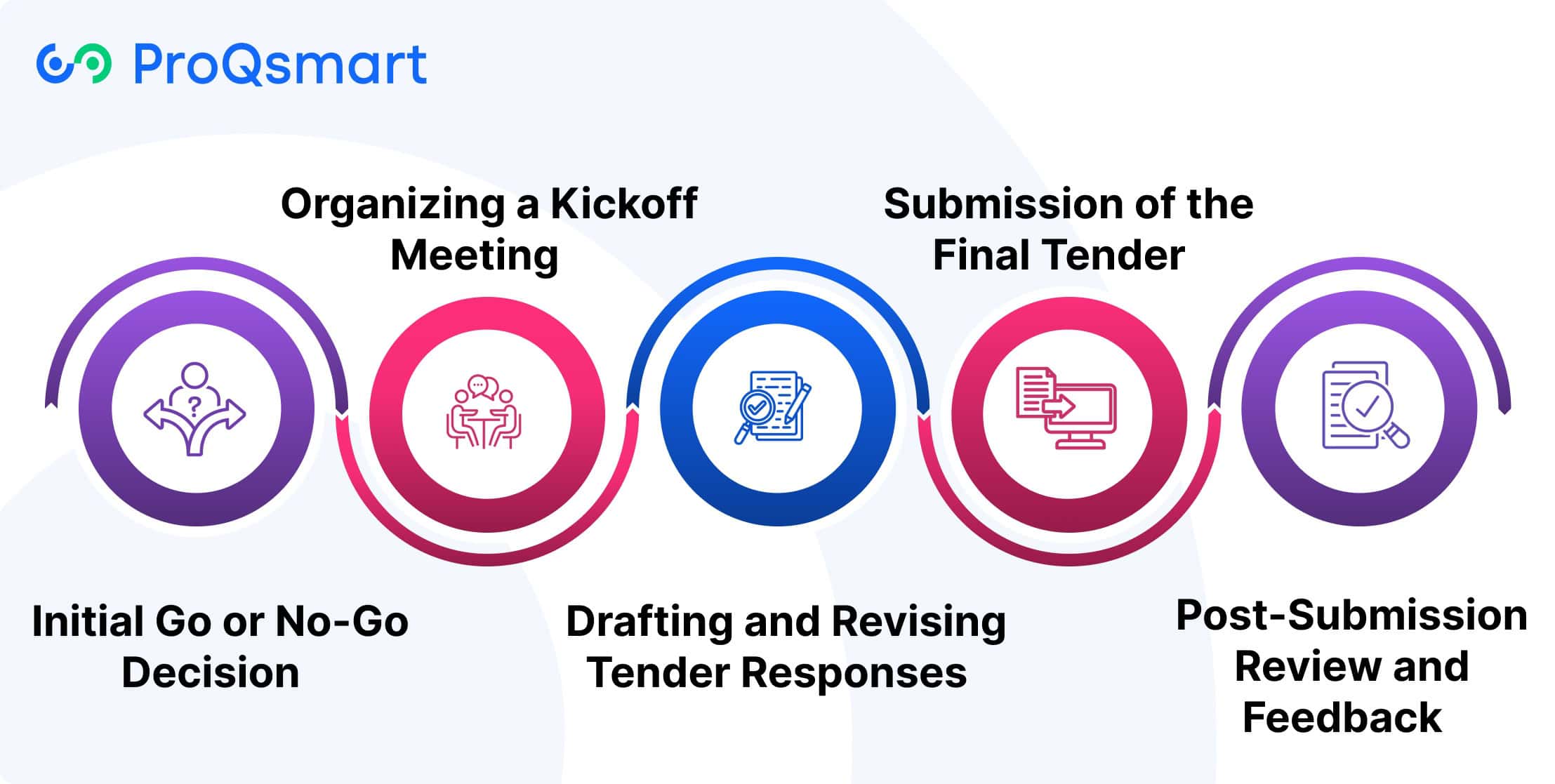
The tender management process involves six key stages, all of which play an equally important role in delivering success. In the U.S., this process begins with the issuance of a Request for Proposal (RFP).
At the same time, an Invitation to Tender (ITT) leads the way for potential suppliers to prepare and submit their bids. Following each stage step by step helps save time, money, and maintain compliance while achieving the best results.
Meticulous documentation at each stage protects due diligence, transparency, and compliance with federal law.
1. Initial Go or No-Go Decision
Deciding whether to pursue a tender involves evaluating organizational capabilities, resource availability, and alignment with strategic goals. Stakeholder input is vital to assess feasibility and prioritize efforts.
A structured framework, such as scoring criteria for financial impact, technical fit, and market positioning, provides clarity. For example, skipping this step risks misallocating resources to unviable projects, leading to inefficiencies later.
2. Organizing a Kickoff Meeting
A well-planned kickoff meeting sets clear expectations about goals, roles, and timelines right from the start. Involvement and collaboration between departments—procurement, legal, marketing—creates buy in and keeps everyone on the same page.
Documenting outcomes provides a roadmap, clarifying responsibilities and action items. For example, providing ownership for the Pre-Qualification Questionnaire (PQQ) that filters suppliers avoids bottlenecks and confusion.
3. Drafting and Revising Tender Responses
While crafting responses, every word matters. Start by answering the obvious questions, usually 80% of the tender right there, and then sharpen the point with a few drafts.
Maximizing clarity by incorporating team feedback and maximizing competitiveness through client-focused evaluation criteria. With ProQsmart’s AI-powered e-tendering tool, this process becomes much more efficient, maintaining compliance while improving collaboration and consistency.
"Tired of Tendering Hassles? Simplify Your Process with Our Expert Checklist - Download Now!"
4. Submission of the Final Tender
Timely submission is not up for discussion, with hard deadlines and no margin for error in tendering. A thorough final check kills mistakes in their tracks, and polished presentation builds trust with decision-makers.
For example, ProQsmart’s robust document management and automation features streamline submission processes and workflows to maintain submission accuracy.
5. Post-Submission Review and Feedback
Post-submission analysis helps to identify strengths and areas for improvement. Collecting feedback—from internal departments and clients alike—helps hone strategies going forward.
Whether it’s better supplier pre-qualification or closer tailoring to ITT requirements, documenting lessons learned promotes a culture of constant improvement.
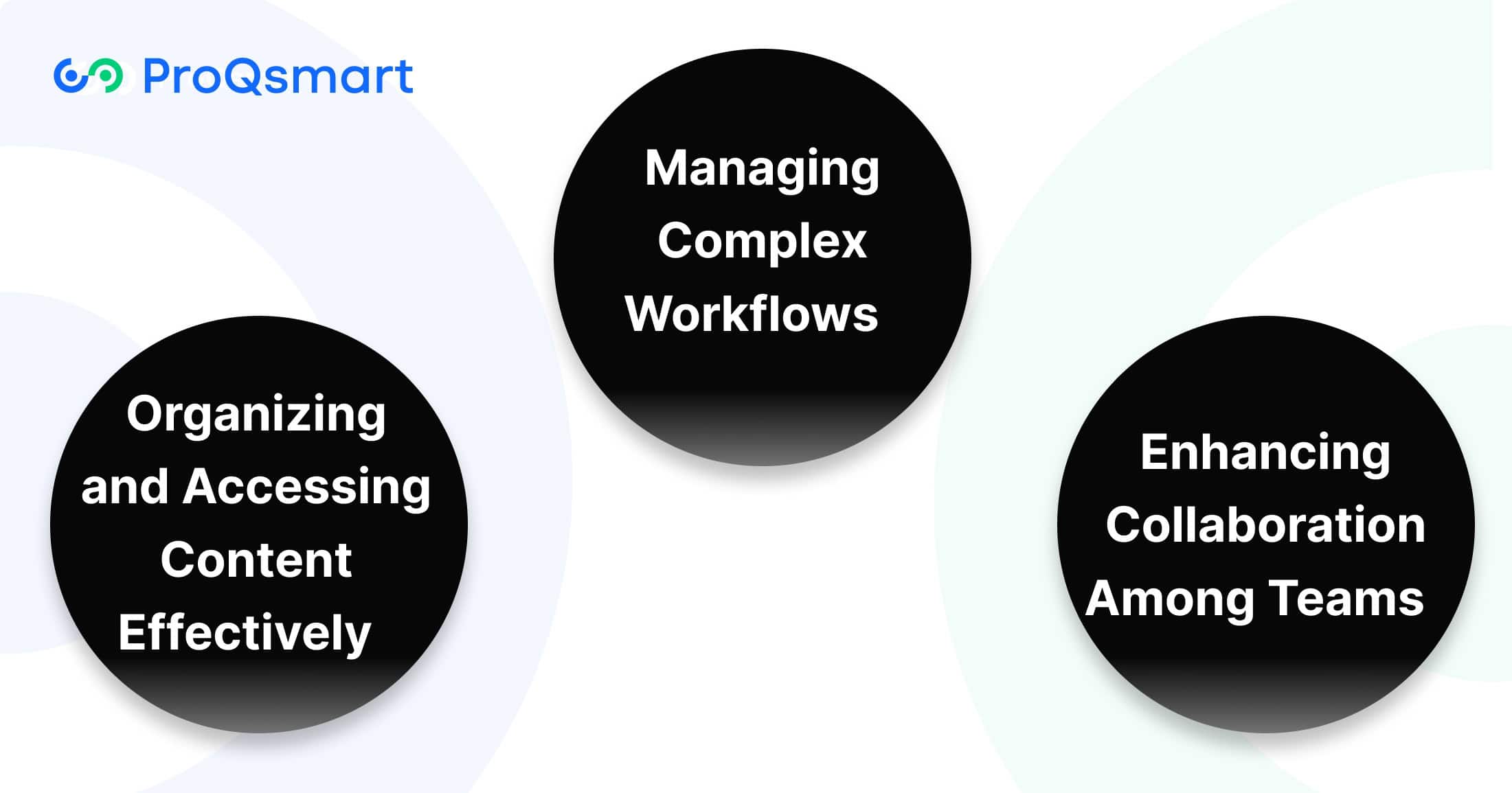
Common Challenges in Tender Management
Tender management can be a complex and demanding process, usually with very tight timeframes and constant pressure to perform. It’s a challenge requiring you to rally different teams, ensure transparency, handle massive documentation, and do so under tight compliance standards. Here, we dive into some of the biggest challenges and practical steps to address them.
Managing Complex Workflows
When you have complex workflows that require input from multiple departments, the tendering process can become cumbersome and time-consuming. The process of simplifying these workflows starts with understanding how to lay out simple, repeatable processes that outline what each team is responsible for.
This is where technology comes into play. Solutions such as ProQsmart automate workflows and cut down on tedious manual processes, making operations more efficient and less error-prone. Documentation, like templates and step-by-step process guides, can go a long way in making the process even more efficient.
Periodic re-evaluations of these workflows are important to pivot with evolving project needs or new state and federal regulations. For example, if you create processes to include subcontractor management from the start, it’s a smoother transition.
Enhancing Collaboration Among Teams
Collaboration is key for successful tender management. A typical incident response team includes members from the procurement, legal, and IT departments. Best practices include establishing transparent communication channels and utilizing shared platforms, like ProQsmart, for real-time teamwork.
Scheduling regular check-ins to address progress and challenges is also essential. Shared tools not only make overlapping efforts more efficient, they help build a sense of accountability and urgency to meet deadlines while upholding high standards.
Organizing and Accessing Content Effectively
Since tender responses can include hundreds of interlinked documents, organization is key. ProQsmart’s E-tenders module acts as a centralized document management system. It serves as a single source of truth by centralizing key documents and company-wide insights.
Smart categorization and tagging help make information easy to retrieve, and regular updates keep it fresh. Since about 80% of tender questions are the same, having this information available at the click of a button reduces time spent responding and reduces mistakes in responses.
Best Practices for Successful Tender Management
Thorough, successful tender management is the bedrock to a successful, efficient procurement department. By implementing best practices and prioritizing strategic areas, organizations can set themselves up for more successful outcomes in competitive bidding.
Understand Project Requirements Thoroughly
Expanding on this, a deep dive into project specifications is the first step toward successful tender responses. Understanding complex specifications gives you the opportunity to develop bids that meet clients’ needs and stand out from competitors. By addressing the ambiguities and unclear aspects early in the process, you reduce the risk of misinterpretation, which could lead to an inaccuracy.
If a construction tender requires certain environmental compliance, knowing the ins and outs of these requirements is important. It minimizes risks and better positions the project to achieve its intended goals.
Focus on Tenders You Can Deliver
Focusing on tenders that suit your skills and experience gives you the best chance of winning. Selective bidding saves time and money by focusing resources where they’re needed most. Taking stock of internal capabilities before deciding to pursue a tender for a major infrastructure project ensures you’re positioned for deliverability right out of the gate.
By taking this approach there are fewer resources wasted and reputation is protected.
Develop a Collaborative Response Plan
Create a clear workflow of roles within your team to facilitate smooth tender responses. By assigning clear responsibilities, setting timelines, and maintaining communication you keep everyone on the same page. Centralized collaboration tools, such as ProQsmart, allow for real-time updates, keeping each member of your team informed and on the same page.
Maintain Clear and Concise Documentation
Thoughtfully assembled documentation is not only persuasive. It establishes your credibility. Create accessibility-friendly materials. Use plain language, large text, and easy to understand formatting and organization.
Concise, clear proposals not only look more professional, but improve understanding, which is essential in any evaluation process.
Ensure Effective Communication Strategies
- Schedule regular updates for stakeholders.
- Address concerns through open communication channels.
- Use feedback loops to refine processes.
Role of Technology in Tender Management
Tender management has changed drastically in modern times with technology at the forefront of revolutionizing how organizations manage procurement processes. Through the adoption of digital solutions, organizations can realize enhanced efficiency, transparency, and competitiveness in their tendering activities.
Join us as we explore further the ways technology is changing the game when it comes to effective tender management.
Benefits of Digital Solutions for Buyers
For buyers, transitioning to digital tender management tools takes a lot of the complexity out of the process. By standardizing formats and enabling side-by-side comparisons, these solutions facilitate faster bid evaluations.
For example, an automated system can immediately rank proposals based on pre-defined criteria, saving valuable time. Automation further removes time-consuming manual tasks such as document storage, lowering the risk of errors and maintaining conformance with procurement policies.
Second, real-time access to data is a game-changer. For buyers, real-time visibility into submissions helps track key performance indicators and quickly provide informed decision-making.
ProQsmart, for instance, offers sophisticated AI-powered analytics that improve and facilitate smarter decision-making, all while fostering transparency through workflows. Its e-tendering and supplier performance monitoring capabilities empower buyers to be proactive while still maintaining operational efficiency.
Advantages for Bidders Using Technology
Digital platforms level the playing field for bidders themselves by making it easier to submit a bid. Instead of handling large physical documents, contractors can submit their proposals much more securely with online tools.
In addition to increasing efficiency through better communication with buyers using instant messaging and notifications to avoid unnecessary delays, these platforms enhance communication.
Technology promotes competitiveness by allowing bidders to better match their proposals with what buyers are looking for. ProQsmart’s supplier relationship management tools, like bid history, arm contractors with the insights to meet buyers’ needs, resulting in more responsive bids.
Bidders are able to submit informed, thoughtful, and effective bids that genuinely shine in competitive scenarios. They do this by leveraging core functionalities including subcontractor management and bill of quantities tracking.
Features to Look for in Tender Tools
When selecting tender management tools, prioritize these essential features:
- User-friendly interfaces: Simplify navigation to reduce learning curves.
- Automation capabilities: Reduce repetitive tasks and ensure compliance.
- Reporting and analytics: Provide actionable insights for decision-making.
- System integration: Ensure seamless operations with existing enterprise tools.
ProQsmart truly shines in this regard, combining extensive intuitive design with robust functionality to address a wide range of procurement needs.
Future Trends in Tender Management
As the procurement landscape continues to change, so too does tender management. These new trends are changing the way we manage bids. Yet they underscore the desire to be nimble and innovative to remain competitive. By adopting these innovations, agencies can improve efficiency, transparency, and outcomes.
Emerging Technologies Shaping the Process
Here are some ways technology is changing the tender management landscape. Today, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are becoming part of the bid evaluation process, providing predictive analysis using past data. This gives teams the ability to fine-tune strategies and predict project results with a level of precision never thought possible.
For example, collaborative AI tools that enable multi-agent collaboration function as a larger, better team—this saves costs and increases efficiency for the bid. In fact, by 2026, 80% of companies are predicted to use AI as part of the tendering process. That’s why it’s important to keep up with innovations such as blockchain.
The increased transparency and security provided by blockchain technology, through the generation of tamper-proof records, are essential in establishing trust within highly competitive bidding environments. ProQsmart is a perfect example of this trend. It makes e-tenders easier, automates complex workflows and allows for real-time collaboration, all while ensuring compliance with speed and efficiency.
Further features such as subcontractor management and supplier performance monitoring help to maximize procurement operations, tailored to budget-driven objectives.
Increasing Importance of Adaptability and Innovation
Adaptability will be key to countering economic downturns and new regulatory pressures. As we move into 2025, expect to see even more sharpened competition and new hurdles to overcome. Innovation encourages new ways to be efficient, creating endless momentum for improvement among the staff.
Proactive planning, backed by new technological capabilities such as artificial intelligence, will help organizations address these complexities to not only survive, but thrive in the long run.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective tender management is crucial for winning opportunities and establishing strong relationships with vendors. By combining a well-defined process, solid partnerships, and the best technology, even the most complex projects can be streamlined. Each step, from preparation to evaluation, requires a thoughtful approach, and overcoming challenges demands foresight and adaptability. This not only leads to more robust products but also increases confidence with stakeholders.
Technology plays a central role in enhancing efficiency and minimizing risk, and its influence will only grow as automation and data analytics become more prevalent. To achieve continued success, it’s essential to be proactive in these shifts and continually improve your approach.
The time and energy you invest in strategic tender management will yield superior outcomes, robust vendor relationships, and sustained success. Ready to take your tender management to the next level? Book a demo with ProQsmart today to discover how ProQsmart’s e-tendering solutions can streamline your tender processes.