A purchase order (PO) is a crucial document in procurement, serving as an official request from a buyer to a vendor for goods or services. It outlines key details such as quantities, unit prices, and delivery timelines, creating a clear and binding agreement between both parties. Acting as both a legal contract and a tool for mutual understanding, purchase orders protect buyers and sellers by setting clear expectations and reducing the risk of disputes.
Beyond its role as a transactional document, a purchase order is a vital component of efficient procurement processes. It helps businesses streamline operations by providing a standardized method for tracking orders, managing budgets, and maintaining accurate financial records. Whether you’re managing inventory in manufacturing or sourcing materials for construction, mastering the use of purchase orders is essential for minimizing errors and fostering strong supplier relationships.
This article will explore everything you need to know about purchase orders—types, processes, benefits, and how technology can enhance their management—empowering you to optimize your procurement strategy.
What is a Purchase Order?
A purchase order (PO) is an official document, controlling the purchase of products or services from supplier(s) to customer(s). This document is integral to the entire procurement process. After acceptance, it functions as a binding contract, detailing the terms of the sale, including price, payment terms, and shipping directions.
A purchase order (PO) is the first step of the purchase-to-pay process in most enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. It’s often the first step that ensures transactions are orderly and traceable.
Key components of a purchase order include detailed information, such as
-
Item descriptions
-
Quantities
-
Unit prices
-
Delivery dates
-
Supplier information
These pieces set clear expectations, helping to avoid miscommunication down the road. For example, a manufacturer ordering steel can use a PO to specify exact grade, weight, and delivery timelines, ensuring alignment with the supplier.
Purchase orders help to improve communication by establishing a clear, standardized process that both parties understand and follow. Between these guidelines and their transparency into budgeting and accounting, they’re invaluable to tracking and managing purchases.
Companies that have implemented e-procurement software solutions are able to create purchase orders digitally. This makes approvals faster and gives your team real-time information on order status.
Understand the Purchase Order Process
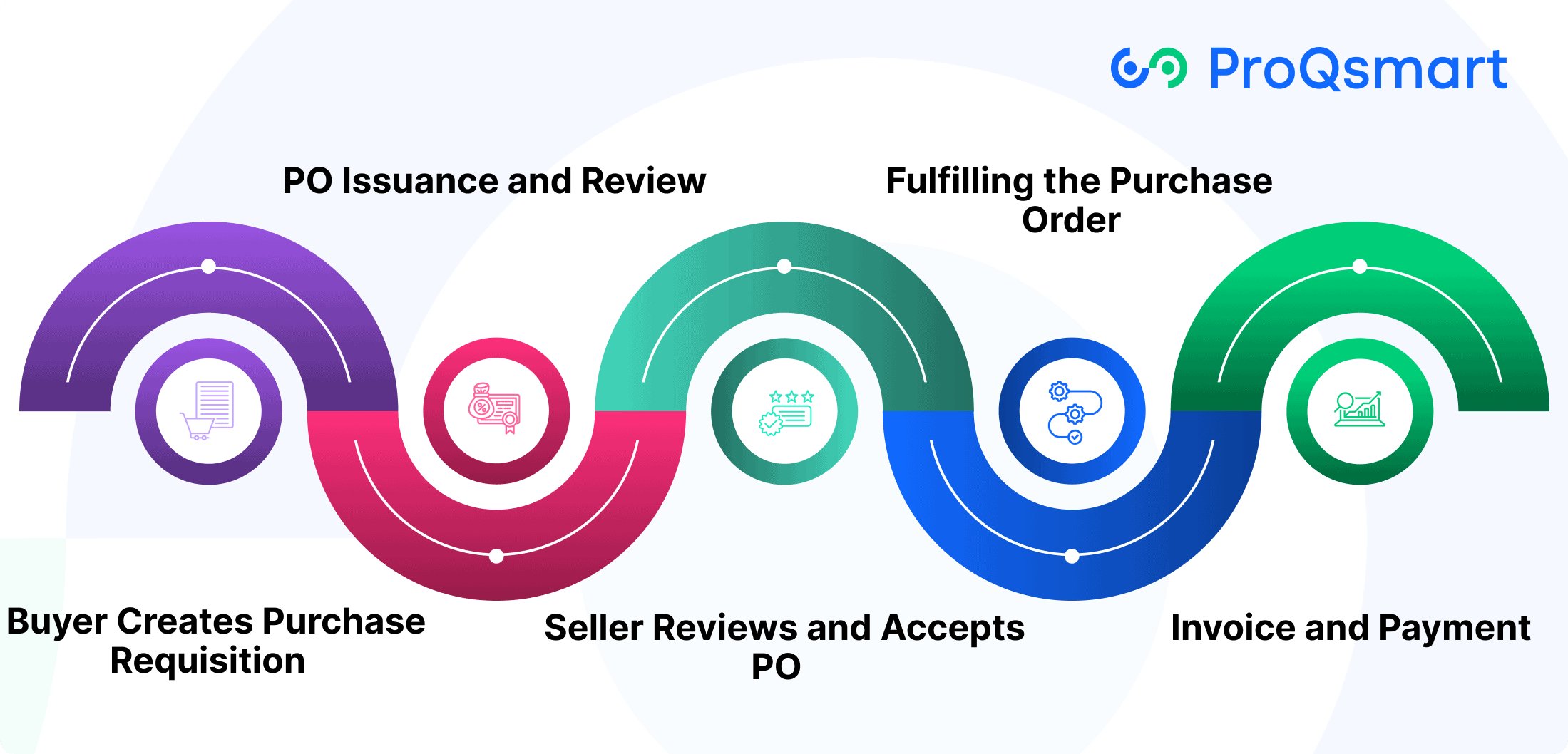
An efficiently run purchase order system minimizes order errors and manual effort. When executed correctly, it can lower procurement expenses by as much as 30%. Here, we outline each step in the purchase order creation process to provide practical tips.
1. Buyer Creates Purchase Requisition
The process starts with determining the need for a good or service. Buyers record details like quantity needed, when they need it, and any special instructions in the purchase requisition.
Well defined and articulated requisitions are necessary to prevent miscommunication or mistakes downstream that everyone will pay for in the end. For instance, saying that you want “100 steel rods, 12-feet long, delivered by November 15” leaves no room for mistakes.
This straightforward specification lays the groundwork for strong, smart procurement.
2. PO Issuance and Review
After the requisition is approved, we process the requisition to PO real fast. Next, we scrub the details from top to bottom—item descriptions, pricing, terms and conditions.
One small mistake can throw the entire workflow out of balance, which is why double or triple checking is key. Authorized managers then authorize the PO, making sure it is in line with budget expectations and compliance requirements in place.
3. Seller Reviews and Accepts PO
The seller reviews the PO to assure that they can meet the buyer’s needs. Timely acceptance of bid creates goodwill, yet rejection creates unnecessary delay which could damage relationship or hurt reputation.
Tools like ProQsmart make this step easy by promoting proactive communication and visibility in real-time.
4. Fulfilling the Purchase Order
Once the order is accepted, the seller proceeds to produce and deliver the order according to the terms agreed mutually. Keeping to timelines and constant communication of progress are essential.
Missing timelines and having to change a promise can lead to serious customer backlash.
5. Invoice and Payment
The supplier creates an invoice that corresponds with the info on the PO and payment is made according to previously agreed upon payment terms.
Doing so leads to mutually beneficial trust and less administrative re-pursuit of payments! Digital PO systems greatly simplify this process, lightening the load for accounts payable teams.
Key Elements of a Purchase Order
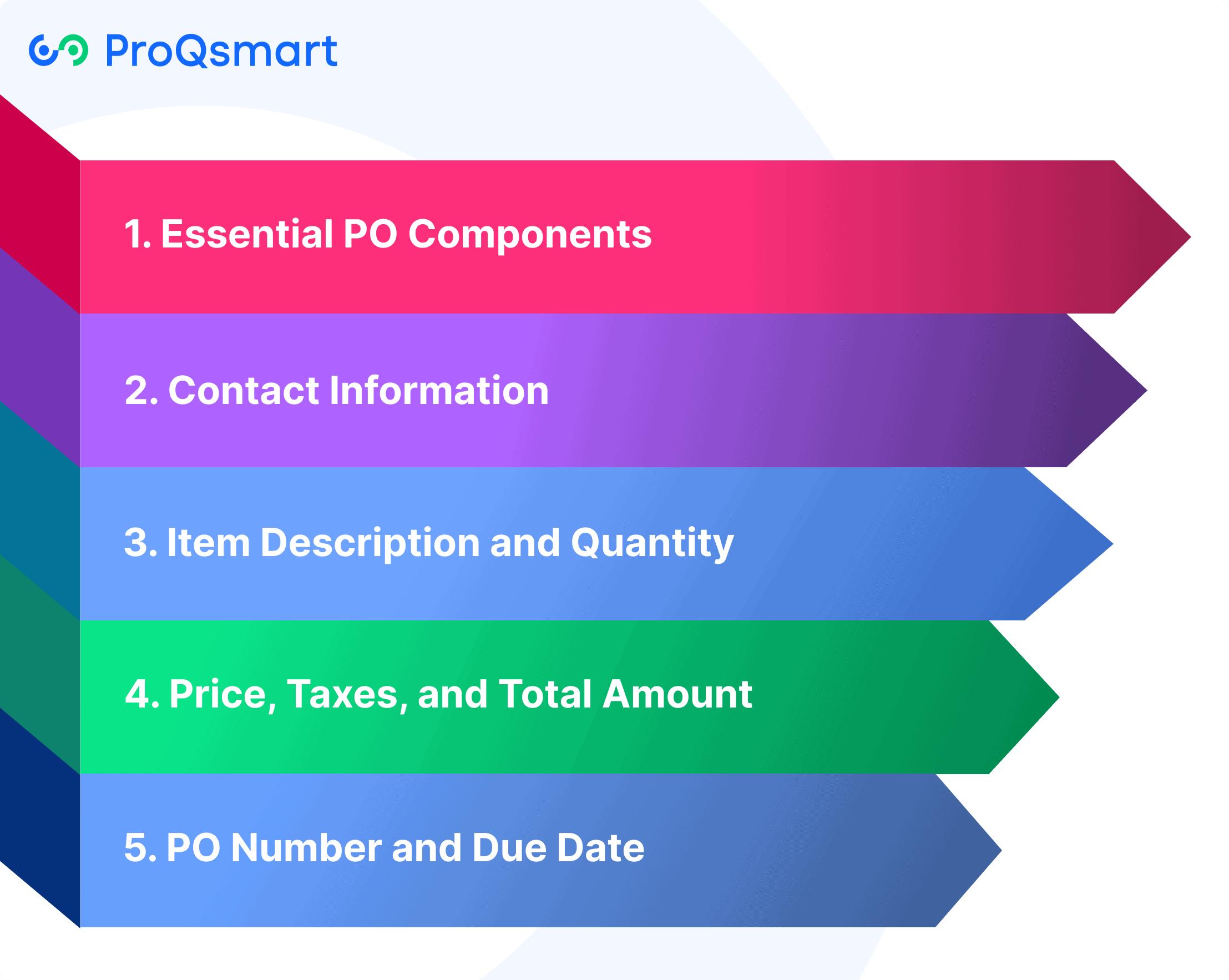
There’s no denying that a purchase order (PO) is a key component of procurement. It serves as an unambiguous roadmap for all transactions between the buyer and supplier. Further, it provides consistency, integrity, and accountability across the full procurement continuum.
To fulfill its intended function, a PO should contain an array of key elements. Each element serves an important purpose in making the process more efficient while reducing potential liability.
1. Essential PO Components
A properly constructed purchase order (PO) has some basic elements. These include aspects such as the buyer and supplier’s information, item description, quantities, pricing, terms of payment, and delivery. Together, each component serves to make sure that everyone’s expectations are known and upheld.
For example, adding long-form product descriptions with SKU numbers prevents mucking things up, especially when ordering raw materials. Failing to include key information may result in disagreements or hold-ups, making attention to detail essential.
Industry best practices suggest that these purchase orders use clear, unambiguous terms. Furthermore, providing a defined and transparent paper trail promotes accountability and facilitates adherence to competitive and regulatory standards.
2. Contact Information
Providing accurate contact information for both the purchasing organization and supplier helps ensure effective communication. Concise, thorough details reduce the chances of incorrect interpretation when the order is being processed.
They also provide the best path to clearing up disputes. For instance, if a contract has no point of contact and someone needs clarification on shipping dates, it could lead to a lengthy disruption in operations.
3. Item Description and Quantity
Detailed descriptions and specific quantities are important. If an item is available only in packages of 10, mentioning this allows for better inventory planning.
Inaccurate, vague descriptions frequently create errors in orders that could ultimately lead to customer dissatisfaction and even lost revenue.
4. Price, Taxes, and Total Amount
Visibility into pricing, such as unit prices, taxes, and any applicable discounts, builds confidence. If you clearly state that a uniform price applies to each collection of items, it helps prevent costly arguments.
Any changes in pricing threaten cash flow or lead to payment delays.
5. PO Number and Due Date
Choosing a unique PO number helps easily track and reference it. Assigning due dates brings attention to required timelines, including delivery and payment.
Both elements are integral to creating productive procurement workflow efficiencies and leading a healthy, financially-responsible organization.
Types of Purchase Orders Explained
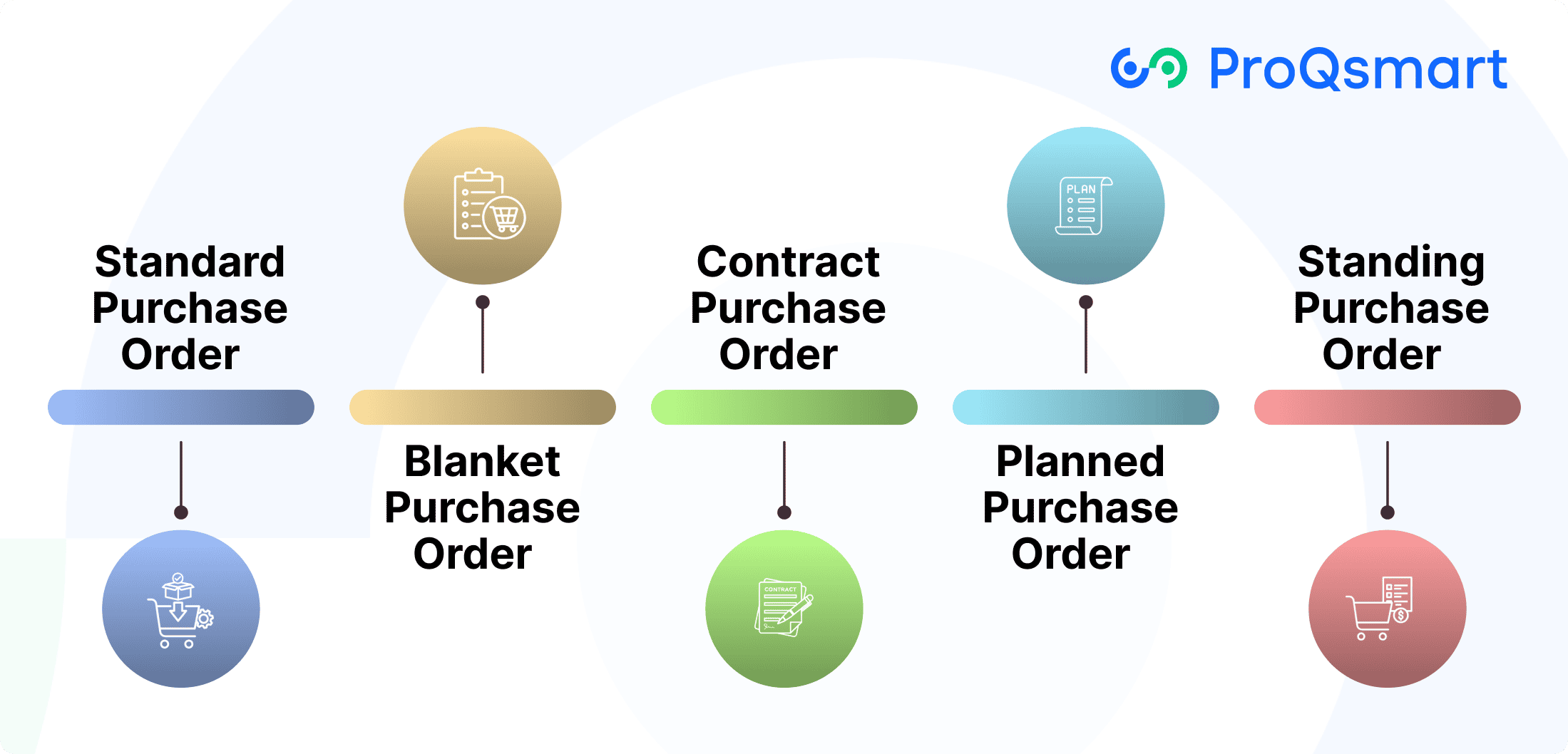
Each one has its own specific purpose and advantages, providing distinct benefits to fulfill the diversified needs of an array of businesses. We’re breaking down each of the five purchase order types below, including the digital purchase orders, and when you should use them.
1. Standard Purchase Order
The most commonly used type, the standard purchase order (SPO) works best for one-time purchases. It serves as a contract, stipulating specific terms such as quantities, prices, and delivery schedules.
For example, businesses usually prefer SPOs for simple purchases, like ordering office supplies or equipment. The simplicity and clarity of SPOs make them particularly useful for new procurement teams, providing a structured approach to purchasing.
For example, a heavy construction company might issue an SPO to buy all the materials they will use on one highway project.
2. Blanket Purchase Order
A blanket purchase order (BPO) operates as a sort of long-term contract for repeat business. This type is especially useful for SaaS subscriptions so that budgets can match up with ongoing expenses.
By setting terms in advance, BPOs make things easier and save time while helping create more trusted relationships with suppliers. For example, a national retail store might issue a BPO to ensure an adequate supply of a certain product is available at all outlets.
3. Contract Purchase Order
Contract purchase orders (CPOs) formalize terms and conditions for future transactions while providing flexibility in payment and delivery arrangements. They protect you by minimizing the risks of disagreements through clearly stipulating expectations.
A software development company, such as one that creates bespoke software solutions, perhaps would use a CPO to oversee the procurement of tailored software applications.
4. Planned Purchase Order
Unlike standard purchase orders, planned purchase orders (PPOs) serve as guidelines for ordering while not holding the ministry to specific order dates or quantities.
This flexibility is extremely valuable for just-in-time inventory strategies, allowing companies to modify POs and receive goods just as demand patterns change.
5. Standing Purchase Order
Open purchase orders are used when you have continuous, on-demand needs and you order the same things repeatedly.
These contracts make future reordering more efficient and help ensure operational continuity, particularly for commonly used goods such as office supplies or raw materials.
PO vs. Related Documents
In procurement, understanding the distinctions between purchase orders (POs) and related documents like invoices, sales orders, and contracts is critical for smooth operations and accurate record-keeping. Using a purchase order system ensures that each of these documents serves its unique purpose at varying stages of the purchasing process.
1. Purchase Order vs. Invoice
A purchase order is an agreement that specifies the goods they wish to purchase. At the same time, the seller issues a pay request invoice so that they can get paid. A PO specifies details such as the items, quantities, prices, and delivery dates, whereas an invoice confirms what has been delivered and the payment due.
Two- or three-way matching POs with invoices and receipt of goods matching prevents inflation of invoices, minimizing errors or disputes. For instance, differences in the quantity received for each line item might lead to delayed payment and put a real strain on vendors.
Being open and honest with vendors ahead of time can help mitigate these problems and generate goodwill, creativity, and collaboration.
2. Purchase Order vs. Sales Order
The RPPO buyer creates a PO. In reply, upon receiving a confirmed order, the seller generates a sales order. While the PO is used by the buyer to convey their requirements, the sales order details the commitment from the seller to fulfill those requirements.
Clarity in each of these documents is incredibly important to prevent misinterpretations. One example is when a delivery date on a PO and a sales order do not match; this leaks into larger supply chain issues.
With ProQsmart’s real-time collaboration tools that keep everyone aligned—all while tracking activities—these risks are greatly reduced.
3. Purchase Order vs. Contract
While a contract creates an overall legal structure, specifically laying out terms for repeated exchanges or interactions, a PO is tied to the one transaction. A CPO, or contract purchase order, provides very flexible terms.
Unlike in a PPO, or planned purchase order, it lacks itemized details – the bread and butter of the transactional phase. Companies typically utilize contracts for agreements with vendors on a longer-term continuum and POs for purchases on an individual transactional basis to enforce adherence and culpability.
Benefits of Using Automation in Purchase Order Process
- Automation in the purchase order (PO) process eliminates manual tasks, reducing errors and improving accuracy.
- Automated systems ensure requisitions are converted into POs efficiently, speeding up the procurement cycle.
- The average PO cycle time is reduced by up to 50%, enabling faster order processing and delivery.
- Procurement teams can focus on strategic activities rather than repetitive administrative tasks.
- Automation simplifies workflows by automating invoice matching, approvals, and tracking processes.
- Companies adopting automation see a 20% reduction in supplier payment and invoice handling costs.
- Real-time collaboration tools improve supplier communication and performance monitoring.
- Dashboards and reports provide insights into key metrics like order cycle times and supplier spend, enhancing transparency.
- Automation ensures compliance with budgets and procurement policies, reducing financial risks.
- ProQsmart’s automation tools help organizations save billions through better spend management, risk reduction, and operational efficiency.
Automate and Digitize PO Process
Today’s competitive procurement is built on smart and streamlined purchase order (PO) processes. Automation is critical to making this transformation possible. Smart businesses can utilize digital tools to streamline and optimize the PO process.
This method facilitates overcoming traditional pitfalls and realizing quantifiable advantages—including major cost reductions, increased operational effectiveness, and better supplier partnerships. Below, I’ll cover the biggest benefits, steps you can take today, and tools to improve productivity with purchase order automation.
Benefits of PO Automation
Digitizing and automating the PO process makes it easier to create, approve and manage POs. This accelerates the process and eliminates the bottlenecks that manual touchpoints often introduce. This increased efficiency eliminates the chance for manual human error, including incorrect entries or duplicate orders, while preventing potential operational bottlenecks.
In addition, it digitizes and automates invoice processing by 97% accuracy so that vendor payments match procurement information.
Automation helps increase transparency, making it easier for teams to monitor spending and stay within budget—a benefit that three in four organizations say they’ve experienced.
How to Automate PO Creation
Setting up automation begins with selecting robust software tailored to your business needs. Integrating these tools into workflows ensures seamless communication between procurement teams and suppliers.
ProQsmart, for instance, offers AI-powered automation to align procurement with budgets, simplify vendor communication, and manage documents effectively—all critical for monitoring and optimizing processes. Periodic evaluations ensure continuous improvements, fostering a scalable procurement system.
ProQsmart: Streamline Your PO Workflow
ProQsmart is a comprehensive AI-powered procurement platform designed to streamline and optimize the purchase order creation process. With its advanced automation capabilities, ProQsmart eliminates manual processes, enabling organizations to use purchase orders effectively while collaborating with suppliers to achieve the best value. The platform offers real-time order tracking, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the purchasing process.
ProQsmart’s budget alignment tools help businesses stay within financial limits while maintaining compliance with procurement policies. Its robust subcontractor management and digital purchase order system improve efficiency by simplifying complex tasks, saving both time and money. Additionally, ProQsmart fosters better supplier collaboration through real-time communication tools and performance monitoring.
By providing actionable insights via dashboards and reports, ProQsmart empowers procurement teams to make data-driven decisions. The platform’s ability to compare quotes, track expenses, and analyze spending patterns ensures informed choices that optimize procurement strategies. Whether it’s managing tenders or ensuring regulatory compliance, ProQsmart delivers a seamless, transparent, and efficient procurement experience tailored to modern business needs.
Conclusion
Purchase orders are more than just a necessary document; they centralize buying, simplify spending tracking, and foster healthy supplier relationships. Understanding the process and leveraging the right tools can significantly save time and maximize cost savings, providing greater flexibility and control over operations. Automated systems further enhance this by reducing human error, speeding up approvals, and improving accuracy.
To take your procurement to the next level, consider ProQsmart. Our innovative platform automates workflows, enhances supplier collaboration, and provides real-time insights into your procurement processes. By streamlining your purchase order management with ProQsmart, you can unlock even greater efficiency and cost savings.
Ready to transform your procurement operations? Book a demo with ProQsmart today!