Open tendering is a widely recognized procurement process that plays a crucial role in promoting transparency and fostering competitive bidding among suppliers. By allowing all qualified vendors to participate, open tendering creates an inclusive environment where businesses of all sizes can compete for contracts, ultimately delivering the best value for taxpayers’ dollars in goods and services.
This method is particularly favored for public sector projects and large-scale professional contracts due to its ability to ensure fair competition among bidders. By clearly articulating project requirements and evaluation criteria, open tendering minimizes the risk of confusion or misinterpretation, thereby facilitating compliance with regulatory standards.
Organizations benefit significantly from this competitive marketplace, as it not only helps save taxpayer dollars but also enhances supplier performance. Open tendering equips procurement professionals with a systematic approach to sourcing, ensuring transparency, accountability, and fairness throughout the selection process. This article will explore the intricacies of open tendering as a strategic procurement method in construction, detailing its processes, benefits, challenges, best practices, and future trends.
What Is Open Tendering?
Open tendering is the most transparent and inclusive way to solicit bids on projects or services—any pre-qualified person, firm, or joint venture may submit a tender. This process is purposely designed to be fair by giving all bidders an equal shot.
We make our project goals, needs, and expectations publicly available. This encourages a market-based competitive environment in which suppliers can compete fairly for contract opportunities. Transparency is the third pillar and is critical to building stakeholder confidence in the procurement process and facilitating public trust and accountability.
Key features of open tendering are public advertisement and transparent, established qualification criteria. These provide a level of certainty that promotes inclusivity, opening doors to small businesses and the large businesses that support them.
By making tender documents publicly available, there is greater scrutiny ensuring that all stakeholders can check that all evaluation processes are fair. A formal process provides a framework to make sure all bids are evaluated consistently, fairly, and in compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
New e-tendering tools like ProQsmart make managing bids, evaluating submissions and reporting outcomes more efficient under an open tendering process. This results in a quicker overall procurement cycle.
Steps in the Open Tendering Process
Open tendering is a rigorous, formal procurement method where transparency and competition are crucial, ensuring an effective procurement process through open competition and many bids.
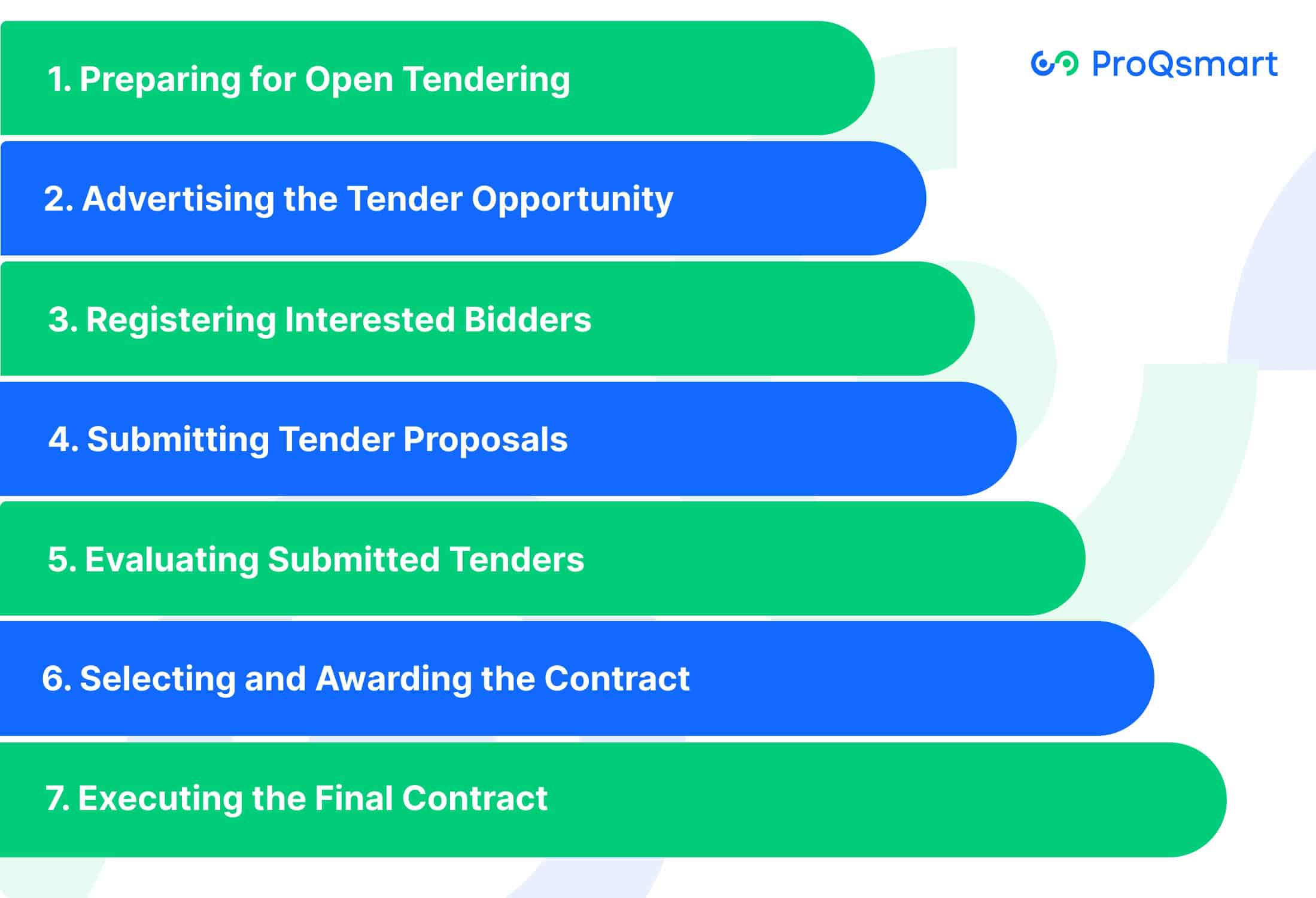
Preparing for open tendering
Advertising the tender opportunity
Registering interested bidders
Submitting tender proposals
Evaluating submitted tenders
Selecting and awarding the contract
Executing the final contract
1. Preparing for Open Tendering
There’s no question that preparation makes all the difference in a successful tender. This stage is where the project requirements are determined in great detail, including scope, quantity, and quality requirements.
Detailed specifications avoid confusion and help meet the desired procurement goal. Engaging relevant stakeholders, such as your financial teams or technical experts, can help you refine your requirements and verify the feasibility of the project.
Setting a budget from the outset is essential to planning realistically and keeping costs in check. As an example, a construction project would need a very tightly defined estimate of material, labor, and contingency costs prior to advertising.
2. Advertising the Tender Opportunity
We advertise all of our tenders on multiple platforms to ensure a competitive and diverse pool of bidders. These can be procurement websites, trade publications, or government portals.
Broadly disseminated advertisements guarantee a level playing field and help create a competitive field. Using plain language in advertisements makes it easier for everyone to understand opportunities, which helps level the playing field and comply with public procurement regulations.
Timing is just as critical—posting opportunities far in advance of deadlines gives bidders the time they need to prepare strong bids.
3. Registering Interested Bidders
Registration is the process of creating a list, or database, of contractors who register their interest. Pre-qualification criteria, like financial stability or past performance, are put in place so that only the most qualified bidders move forward.
Having a transparent process to register increases confidence and facilitates open communication. As an example, an open government project can implement online bidder registration to ease the burden for prospective bidders.
4. Submitting Tender Proposals
Tender submissions have to meet the instructions and deadlines set by the buyer. Proposals usually contain technical specifications, detailed cost estimates, and documentation to support claims made in the proposal.
Bidders need to be responsive to detailed project specifications, showing their ability to comply, work professionally, and more. Bid planning is the most important part.
5. Evaluating Submitted Tenders
Criteria | Description |
Technical Proposal | Alignment with specifications |
Financial Proposal | Cost-effectiveness |
Past Performance | Previous relevant project experience |
Compliance | Adherence to guidelines and deadlines |
Evaluation is where bids are compared according to these criteria. For instance, in an open tender process, applicants submit their proposals first for a qualification review before full bids are accepted.
6. Selecting and Awarding the Contract
Finally, the most responsive and responsible bidder is selected as the most advantageous bidder, taking into account the evaluation results. Contracts are allocated by open competition, in a transparent manner that ensures no favoritism or bias.
Public projects generally are required to post award information in order to show that they are being accountable.
7. Executing the Final Contract
The final step is executing all terms, signing contracts and starting work. Detailed timelines and deliverables are specified to maintain efficient operations.
Conducting regular reviews during execution allows you to catch and work through issues as they arise.
Benefits of Open Tendering
Enhanced Competition: Open tendering invites a wide range of suppliers to submit bids, which fosters a competitive environment. This increased competition can lead to lower prices and better terms for the buyer, as suppliers strive to differentiate themselves and win contracts.
Transparency: The open nature of the tendering process ensures that all suppliers have equal access to information about the tender. This transparency helps to mitigate the risk of favoritism, corruption, or procurement fraud, as all bids are evaluated based on clearly defined criteria available to all participants.
Level Playing Field: Open tendering allows small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to compete alongside larger firms. This inclusivity promotes diversity in the supplier base and supports the growth of smaller businesses, which can bring innovative solutions and local expertise to projects.
Cost Efficiency: By fostering competition among a diverse group of bidders, open tendering often results in significant cost savings for organizations.
Suppliers are motivated to offer their best pricing and value propositions, which can lead to reductions in overall project costs.
Quality Outcomes: The process encourages suppliers to present their best offerings, ensuring that those selected meet high standards of quality and reliability. This focus on quality can lead to better project outcomes and increased satisfaction for stakeholders.
Market Insight: Open tendering provides organizations with valuable insights into market pricing and supplier capabilities. By analyzing bids from various suppliers, procurement teams can make informed decisions based on current market conditions and trends.
Accountability: The structured nature of open tendering increases accountability among all parties involved. Clear documentation and defined evaluation criteria help ensure that decisions are justified and aligned with organizational goals, reducing the potential for disputes.
Accessibility and Diversity: The open tendering process encourages participation from new and emerging contractors, broadening the supplier pool. This not only enhances competition but also allows organizations to benefit from fresh ideas and innovative approaches that smaller or less established firms may offer.
These benefits collectively enhance the effectiveness of the procurement process, making it more equitable and efficient while fostering healthy competition through open tender opportunities in the marketplace.
Challenges in Open Tendering

Managing a High Volume of Bids
Open tendering attracts a large number of suppliers, leading procurement teams to face an overwhelming volume of bids. Each submission may have different terms, cost structures, and technical details, complicating the evaluation process.
This diversity can create significant challenges, as an unsystematic approach to bid evaluation often results in costly delays and wasted resources. To mitigate these issues, it is crucial for teams to establish clear evaluation frameworks tailored to each project’s needs. Involving project stakeholders in creating tender documents ensures alignment with project objectives and reduces errors. Given the complexity of many projects, processing bids can take weeks or even months, even with thorough preparation.
Addressing Limited Supplier Diversity
A third challenge lies in ensuring supplier diversity. Open tendering can lead to a self-perpetuating cycle where the current suppliers are favored and smaller or minority-owned businesses are excluded.
For example, consider a construction project where most bids would only come from established firms, excluding newer vendors with innovative solutions. To address this, procurement teams need to be intentional about advertising the tender across multiple channels.
They need to set evaluation criteria that attract competition from as wide a pool of suppliers as possible. This approach doesn’t just promote inclusion, it brings new ideas to the table and more competitive bids.
Preventing Bid Rigging and Collusion
Open tendering can be compromised by unethical practices such as bid rigging or collusion among suppliers. In these cases, suppliers may coordinate to manipulate the bidding process, agreeing to raise prices or limit competition. This undermines the principles of open tendering, which aim to promote fair competition and transparency.
Such practices distort market conditions, leading to inflated project costs and potentially lower quality of goods and services. Collusion erodes trust in the procurement process, making it difficult for legitimate businesses to compete fairly and diminishing the overall value for money. Addressing these issues is crucial to maintaining the integrity of the procurement system and ensuring it effectively serves its intended purpose.
Overcoming Administrative Complexities
Running open tenders can create a significant administrative burden, involving tasks such as drafting tender documentation and evaluating bid offers. Without the appropriate systems in place, these routine tendering processes can lead to errors and costly project delays, especially in complex projects that require detailed specifications and contractor qualifications.
Comparison with Other Tender Types
Open vs Closed Tendering
Open tendering is often viewed as the most transparent and competitive procurement process available in the construction industry, allowing any qualified supplier to bid. This inclusivity fosters creativity and results in a diverse range of options, enabling firms to fairly compare competing bids in terms of cost, quality, and delivery speed. This is particularly important in public infrastructure projects, where open tendering allows smaller suppliers to compete based on their merits.
In contrast, closed tendering limits participation to a pre-approved list of suppliers. While this approach can streamline the process and reduce administrative burdens, it decreases competition and may lead to less competitive pricing. Closed tendering is typically preferred for projects that require specialized expertise, such as technical upgrades or unique construction tasks, where only a select few suppliers can meet the specific technical requirements.
Restricted and Negotiated Tenders
Restricted tendering further limits competition by shortlisting suppliers using pre-qualification criteria. This hybrid approach strikes the right balance between competition and efficiency, frequently utilized for complex industries such as healthcare, where compliance and technical know-how are paramount.
In contrast, in negotiated tendering, the emphasis is on more direct discussion with one to three suppliers. Although this approach allows for customized solutions, it is time-intensive, often taking months to execute contracts.
A high-profile urban redevelopment project usually needs negotiated tendering. Its high level of complexity and requirement for tailoring further underscores the value of this approach.
Single-Stage and Two-Stage Tenders
Single-stage tendering requires the submission of a full proposal at the outset, making it more appropriate for simpler projects with well-defined needs.
Two-stage is intended for more complicated projects such as large-scale construction. The process begins with some preliminary conversation, leading to a formal bidding period.
Although it can be more flexible, the two-stage tendering method leads to higher costs due to longer timelines.
Best Practices for Open Tendering in Construction
Streamlining the Evaluation Process
A carefully structured and standardized evaluation process is one of the most important components of successful open tendering. Before submitting an open bid, it is crucial to first ascertain a clear understanding of the project scope, required vendor qualifications, and award criteria. This clarity helps avoid wasted effort and ensures that your tender aligns with the client’s expectations in the competitive bidding process.
Focus on the kind of projects that fit your available capacity. This targeted approach will dramatically improve your hit ratio, rather than blindly putting bids in on every listed opportunity.
Submitting a competent tender, with complete and correct documentation, is equally vital. A thorough, well-organized, and timely submission portrays an image of professionalism and can create confidence and trust among potential suppliers. The evaluation process can extend from weeks to months, with typically one to three contractors being evaluated.
Keeping a current and auditable record should be a non-negotiable. Digital tools, such as ProQsmart, make this process quick and easy by storing all tendering data in one place, allowing for easy evaluation, and providing complete audit trails.
Engaging Stakeholders Effectively
Stakeholder engagement starts with transparency. Bringing together these cross-functional teams as early as possible helps ensure that every dimension of the tender is addressed. For example, including project managers and financial teams can ensure the bid meets the company’s operational capabilities and budget constraints.
This teamwork leads to an integrated approach, minimizing mistakes and maximizing informed decisions. Open communication with suppliers builds trust, resulting in compliance and smooth project execution. Platforms such as ProQsmart promote collaboration in real-time, allowing for quick communication to anyone involved in the process.
Leveraging Technology in Procurement
Technology has been a huge equalizer when it comes to open tendering. When digital tools bring together all the bid invites, bid submissions, and communication with suppliers, workflows become streamlined and more time efficient.
ProQsmart’s AI-driven e-tendering system that centralizes document management and supplier evaluations saves time and costs by automating time-consuming processes. Features such as subcontractor management, compliance tracking, and performance monitoring help make the process efficient, effective, and transparent.
Businesses can further monitor budgets in real time, ensuring procurement practices are in line with corporate financial objectives.
Future Trends in Open Tendering for 2025
Role of Digital Solutions in Procurement
Effectively layering new digital solutions onto existing procurement processes will radically reshape open tendering in 2025. AI-powered tools, such as those being developed by ProQsmart, will be instrumental in improving decision-making and streamlining operations. ProQsmart streamline workflows, control documentation, and guarantee compliance with highly detailed sourcing information.
These tools significantly increase speed while creating unprecedented transparency. This, in turn, allows procurement teams to dedicate their time to more strategic priorities, rather than being weighed down by the administrative burdens.
Also ProQsmart’s budget-driven procurement and capital expenditure sourcing features can align procurement with both financial and sustainability objectives, ensuring businesses stay competitive.
Adoption of Data Analytics and Automation
In 2025, data analytics and automation will revolutionize how procurement teams mitigate risk and maintain stability. Predictive analytics will enable teams to anticipate disruptions before they happen. In the meantime, automation will address the issue of a tightening talent pool, with a projected churn rate of 25%.
ProQsmart also provides intelligent supplier performance monitoring and subcontractor management. These tools offer powerful, real-time insights into supplier capabilities, which serve to both mitigate risk and enhance operational efficiency.
Enhancing Collaboration Through Technology
Collaboration, as it always should be, will be at the heart of successful procurement. Platforms such as ProQsmart encourage real-time collaboration, connecting all stakeholders to build productive supplier relationships and simplify communication.
This increased collaboration leads to less rework, faster project delivery, more uniform procurement objectives, and a more transparent supply chain.
Conclusion
Open tendering, for all it’s faults, remains the most transparent and competitive method of sourcing goods and services. It fosters a level playing field, spurs innovation and improves accountability and value for money. With sensible practices and guidance, businesses of all sizes can experience successful, timely execution of projects and the long-lasting benefits that come along with it. Though hurdles such as bid management or keeping up with compliance are real, they can be overcome with the right planning and resources.
There is reason for optimism, as technology increasingly becomes a key factor in improving processes. Being aware of current trends and being open to new innovative solutions will ensure your organization is at the cutting edge. Learn how open tendering can help you meet your objectives and provide consistent outcomes. Get started with ProQsmart’s E-tendering platform today to build a better procurement strategy and build your business success. Book a demo now!