Open tendering increases the public accountability of the procurement process. It opens all contracts to competition by allowing any qualified suppliers the chance to bid, saving taxpayers money in the process. This approach creates a level playing field for competition and fosters greater participation from a diverse pool of suppliers, resulting in cost savings and better supplier relationships.
When businesses practice open tendering, they open themselves up to a wider range of potential vendors. It’s a strategy that encourages innovation and reliability throughout their supply chain. Open tendering further encourages adherence to regulatory guidelines, minimizing the risk of favoritism or narrow sourcing options.
For procurement managers, this method makes it easier to choose vendors while encouraging accountability and efficiency. In a truly competitive market, open tendering increases operational performance. It also ensures the greatest value for products and services, ensuring a long-term successful outcome.
What Is Open Tendering in Procurement?

Open tendering is the most competitive public procurement method, based on principles of fairness and transparency to secure the best value for money for goods or services. It’s about opening up the tender process to full competition by publicizing an Invitation to Tender (ITT) and enabling any qualified supplier or contractor to respond. This process is commonly known as open competitive bidding or open solicitation.
By following established procedures, open tendering promotes equal opportunity among bidders, ensuring decisions are based on merit rather than favoritism. One of the key principles to open tendering is transparency, making sure that all potential participants have the same information available to them.
Comprehensive, unambiguous, and informative bidding documents are critical for preparing suppliers and guiding them through the process. These documents clearly outline requirements, timelines, and evaluation criteria, creating a level playing field.
Key Features of Open Tendering
Open tendering requires transparency to any qualified bidder, regardless of their location—local or foreign. Bidders are required to meet objective qualification criteria, such as financial capacity, technical ability and adherence to legal requirements. Detailed technical specifications allow suppliers to better understand what is expected of them.
At the same time, objective evaluation criteria allow for an impartial evaluation of their proposals. Single-stage tenders need only one bidding round. By comparison, two-stage tenders have a qualification phase that precedes the submission of final bids.
Digital tools make this process easier, allowing wider bid submissions, supplier communications, and evaluations to take place all in one platform.
How does Open tendering impact Procurement process
Open tendering significantly enhances procurement processes by promoting competition among suppliers, which leads to better pricing and value for money. By inviting bids from a wide range of suppliers, organizations can access diverse offerings and innovative solutions that may not be available through closed or restricted tendering methods.
Moreover, open tendering fosters transparency and accountability, reducing the risk of corruption and favoritism. This openness helps build trust with stakeholders and customers, as it demonstrates a commitment to ethical procurement practices. Organizations that adopt open tendering practices are often viewed more favorably, enhancing their reputation in the marketplace.
Additionally, open tendering allows for greater inclusivity, enabling small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to compete for contracts alongside larger firms. This not only supports economic diversity but also encourages local businesses to participate in public procurement.
How Does Open Tendering Work in Procurement
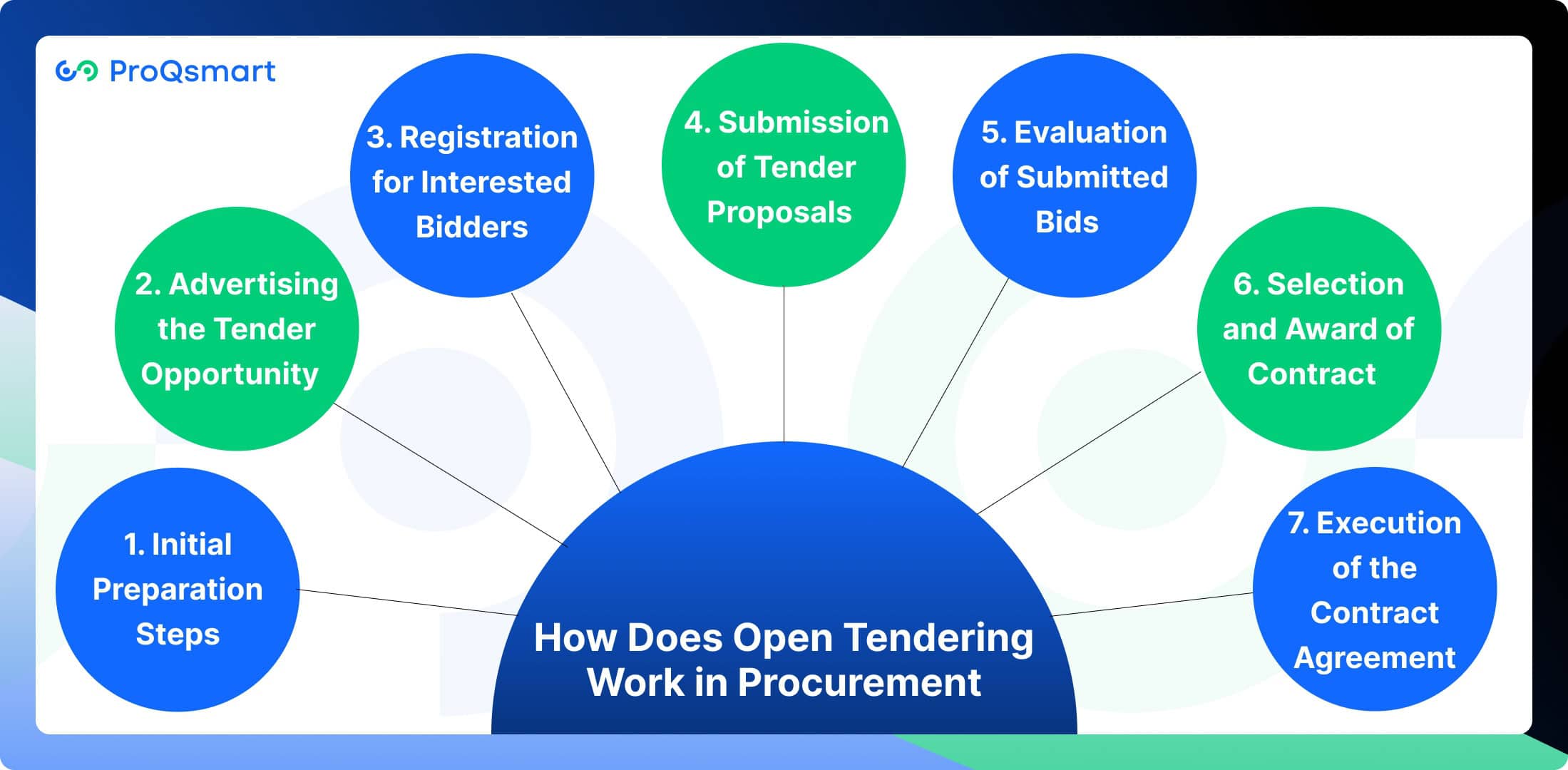
1. Initial Preparation Steps
The open tendering process starts well in advance with careful preparation to lay the appropriate groundwork for clear and transparent processes. Essential tasks include defining project requirements, timelines, and budget constraints.
Understanding the key stakeholders, including procurement officers, project managers is also crucial. Creating clear, unambiguous specifications and evaluation criteria provides direction to bidders and evaluators.
Getting internal approvals ensures that the tender aligns with organizational goals and compliance requirements. Providing clear specifications is extremely important to avoid confusion.
So if a construction project needs energy-efficient materials, that needs to be spelled out in detail to draw the right suppliers. Publicity and detailed criteria guarantee that proposals are evaluated solely on their merit, creating a culture of trust and professionalism.
2. Advertising the Tender Opportunity
Advertising tender opportunities widely is essential in the open tendering process, particularly in the construction, manufacturing, and interior fit-out sectors. Common channels for advertisement include trade publications, government portals, and industry-specific platforms. Each advertisement must provide comprehensive project information, eligibility requirements, deadlines, and contact details to ensure clarity for potential bidders.
Engaging both local and international bidders is crucial for maximizing competition. For instance, when a construction or manufacturing tender is advertised on both regional and global platforms, it attracts a diverse range of suppliers, thereby enhancing competitive bidding. Procurement notices serve as formal invitations to tender, ensuring that all interested parties receive the same information simultaneously.
3. Registration for Interested Bidders
The registration process establishes a formal mechanism to control which bidders are eligible to participate in the tendering process. Registrants must demonstrate proven financial stability and relevant technical expertise to qualify.
For example, a supplier bidding on a construction project may need to provide evidence of their experience and capabilities in similar projects. Maintaining an up-to-date registry of all registered bidders facilitates effective communication regarding future opportunities.
It is essential to set clear deadlines and transparent selection criteria to ensure that only the most qualified participants advance in the bidding process. This approach not only enhances the integrity of the tendering process but also promotes fairness and competition among bidders.
4. Submission of Tender Proposals
Tender submissions require careful documentation, including detailed technical specifications, pricing breakdowns, and compliance forms. Following specific format requirements is essential, as proposals must be presented in a certain way to be accepted.
Meeting deadlines is very important; late submissions are usually rejected outright, so it is crucial to stick to the timeline. Confidentiality also plays a key role in maintaining the integrity of the process. For example, sealed bids help protect sensitive information and prevent trade secrets from being misused.
Thorough checks of compliance requirements ensure that only eligible proposals move on to the evaluation phase. By following these guidelines, organizations can improve the effectiveness and fairness of their tender submissions.
5. Evaluation of Submitted Bids
The table below outlines common criteria:
Criteria | Details |
Technical Quality | Compliance with specifications and project needs. |
Financial Viability | Cost-effectiveness and adherence to budget limits. |
Experience | Supplier’s track record in similar projects. |
Each bid is evaluated according to these criteria. By documenting the entire process, we help hold ourselves accountable and create a knowledge base that informs future tenders.
6. Selection and Award of Contract
The selection process for contracts is typically based on objective criteria, often focusing on the lowest-cost bid that meets the specified requirements. Transparency is crucial in this process, as it fosters trust among stakeholders.
Providing feedback to unsuccessful bidders about why another bidder was chosen helps build goodwill and maintains the potential for future collaboration. Once a successful bidder is identified, the contract formalization process begins.
During this phase, all terms—including deliverables and payment schedules—are clearly outlined to prevent any misunderstandings. This clarity ensures that both parties have a mutual understanding of expectations, contributing to a smoother execution of the contract.
7. Execution of the Contract Agreement
Contract execution refers to the formal signing of agreements that outline the scope, timing, cost, and quality expectations of a project. This step is essential for establishing a legally binding relationship between the contracting parties.
Monitoring compliance is crucial to ensure that the supplier meets their commitments, such as delivery dates and quality standards. For example, if a supplier is providing a complex piece of machinery, ongoing inspections may be necessary to verify adherence to specifications.
Effective contract administration plays a vital role in overseeing the project’s progress. It allows for prompt identification and resolution of any issues that arise, ensuring that the project remains on track for successful completion. By maintaining close oversight during execution, organizations can achieve their project goals and uphold contractual obligations.
Benefits of Open Tendering in Procurement
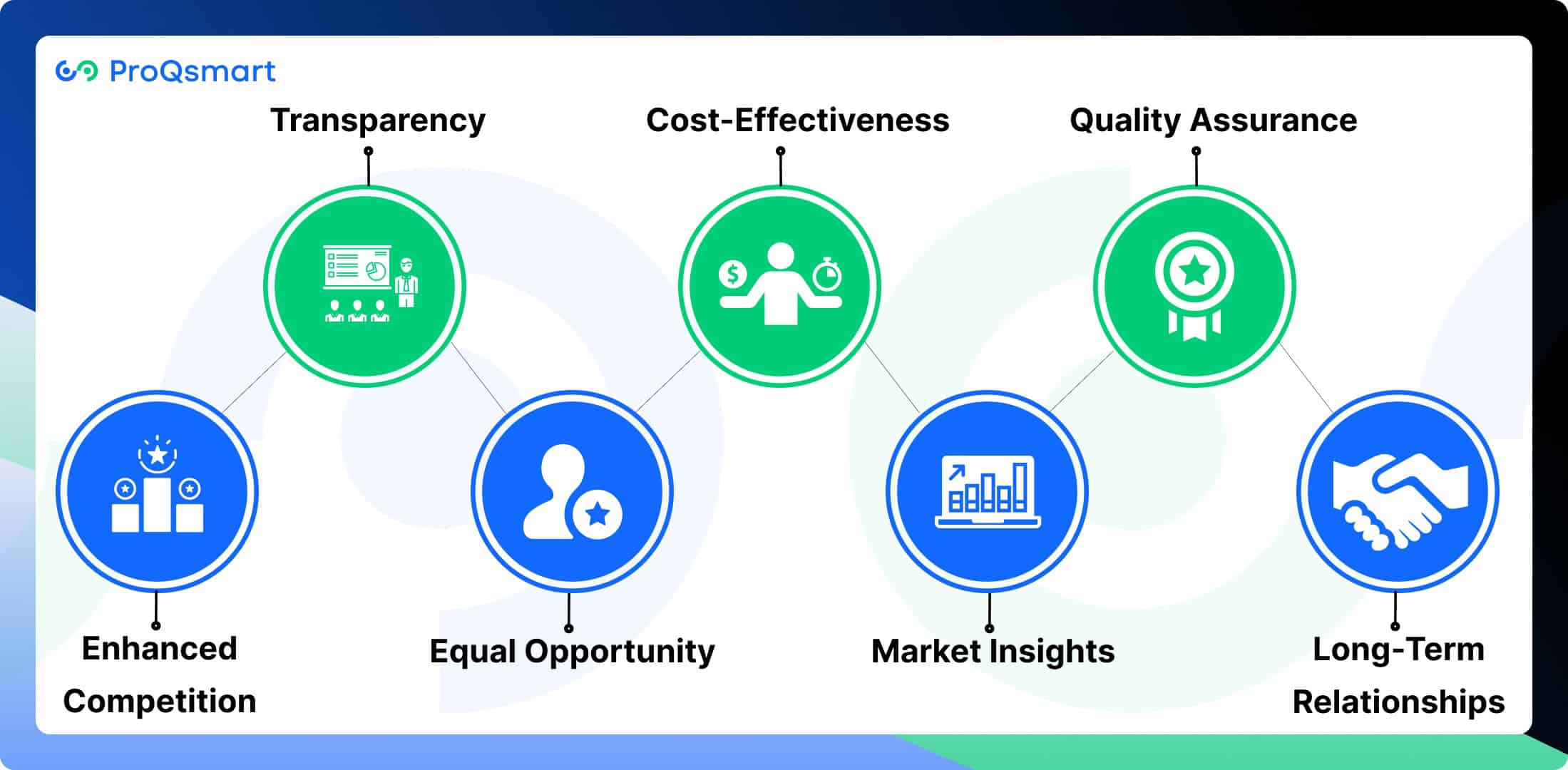
Open tendering is a widely used procurement method that offers several advantages, contributing to a more effective and competitive bidding process. Here are some key benefits:
Enhanced Competition: Open tendering invites a diverse range of suppliers to submit bids, which increases competition. This competitive environment often results in better pricing and improved quality of goods and services, as suppliers strive to present their best offers.
Transparency: The open nature of this process ensures that all qualified bidders have equal access to tender documents and information. This transparency reduces the risk of favoritism or corruption, fostering trust among stakeholders and promoting ethical procurement practices.
Equal Opportunity: Open tendering provides smaller firms with the opportunity to compete alongside larger organizations for contracts.
This inclusivity encourages innovation and allows for a wider variety of solutions, which can be particularly beneficial in specialized projects.
Cost-Effectiveness: By increasing competition among suppliers, open tendering can lead to more favorable pricing. Suppliers are incentivized to offer competitive bids, which can result in significant cost savings for the contracting entity.
Market Insights: The open tendering process allows organizations to gather valuable data on market pricing, supplier capabilities, and industry trends. This information can inform future procurement strategies and decision-making.
Quality Assurance: With a broader pool of bidders, organizations can select suppliers based on rigorous evaluation criteria, ensuring that only those who meet high standards are awarded contracts. This focus on quality helps mitigate risks associated with subpar goods or services.
Long-Term Relationships: The transparency and fairness inherent in open tendering can lead to stronger relationships between organizations and suppliers. By fostering trust and collaboration, organizations may benefit from enhanced service and support over time.
Challenges in Open Tendering
Open tendering can sometimes create distinct challenges, but a fair and measured, systematic approach can lead to great outcomes. Each tender with its requirements is unique, thus making a one-size-fits-all solution impossible. Below, we explore some of the major challenges and ways to overcome them.
Managing High Volumes of Bids
Managing hundreds of bids can inundate procurement teams if workflows cannot be organized properly. As an example, a given construction project could receive hundreds of submissions, each one needing an in-depth analysis.
Adopting effective bid management systems, like e-procurement platforms, can make it easier to sort and track bids. Setting criteria to prioritize bids, such as financial stability or industry-related certifications, guarantees that the chosen project caters most directly to the goals of the project.
Having sufficient resources, such as qualified staff and time, is key to conducting comprehensive evaluations. Without these, critical information will be overlooked, resulting in a poor vendor choice.
Ensuring Supplier Diversity
Promoting supplier diversity presents several challenges that organizations must address to create a more inclusive procurement process. One significant hurdle is the limited awareness among diverse suppliers regarding available opportunities and the open tendering process itself. Many potential participants may not have the resources or knowledge to navigate formal procurement systems, which can result in their under representation in bidding activities. Additionally, diverse suppliers often face barriers such as financial constraints and a lack of experience, making it difficult for them to compete effectively with established vendors.
Risks of Collusion or Bid Rigging
Collusion and other unethical practices pose significant risks to the integrity of the bidding process. Indicators of such behavior may include identical pricing among bidders or suppliers winning contracts in a predictable, alternating pattern. These red flags can undermine competition and lead to inflated costs for the contracting entity.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should implement robust monitoring mechanisms, such as regular audits and whistleblower hotlines, to detect and address any suspicious activities early on. Ensuring transparency and fairness throughout the tendering process is essential for building trust among all participants and preventing unethical practices. By fostering an open environment, organizations can enhance the integrity of their procurement processes and promote fair competition.
Administrative and Time Constraints
Open tendering often involves extensive paperwork, frequent communication, and coordination among various stakeholders, which can quickly consume valuable time and resources. The administrative burden associated with managing these tasks can be overwhelming, potentially leading to delays in the procurement process.
To alleviate these challenges, organizations can leverage automation tools, such as document tracking software, to streamline repetitive tasks and improve efficiency. By automating processes like document submission and communication tracking, teams can focus on more strategic activities rather than getting bogged down in administrative details.
Establishing realistic timelines that reflect the complexity of each tender is also crucial. This approach allows procurement activities to be conducted efficiently while maintaining transparency and fairness throughout the process. By balancing efficiency with thoroughness, organizations can enhance their open tendering practices and achieve better outcomes.
Comparison of Open and Closed Tendering
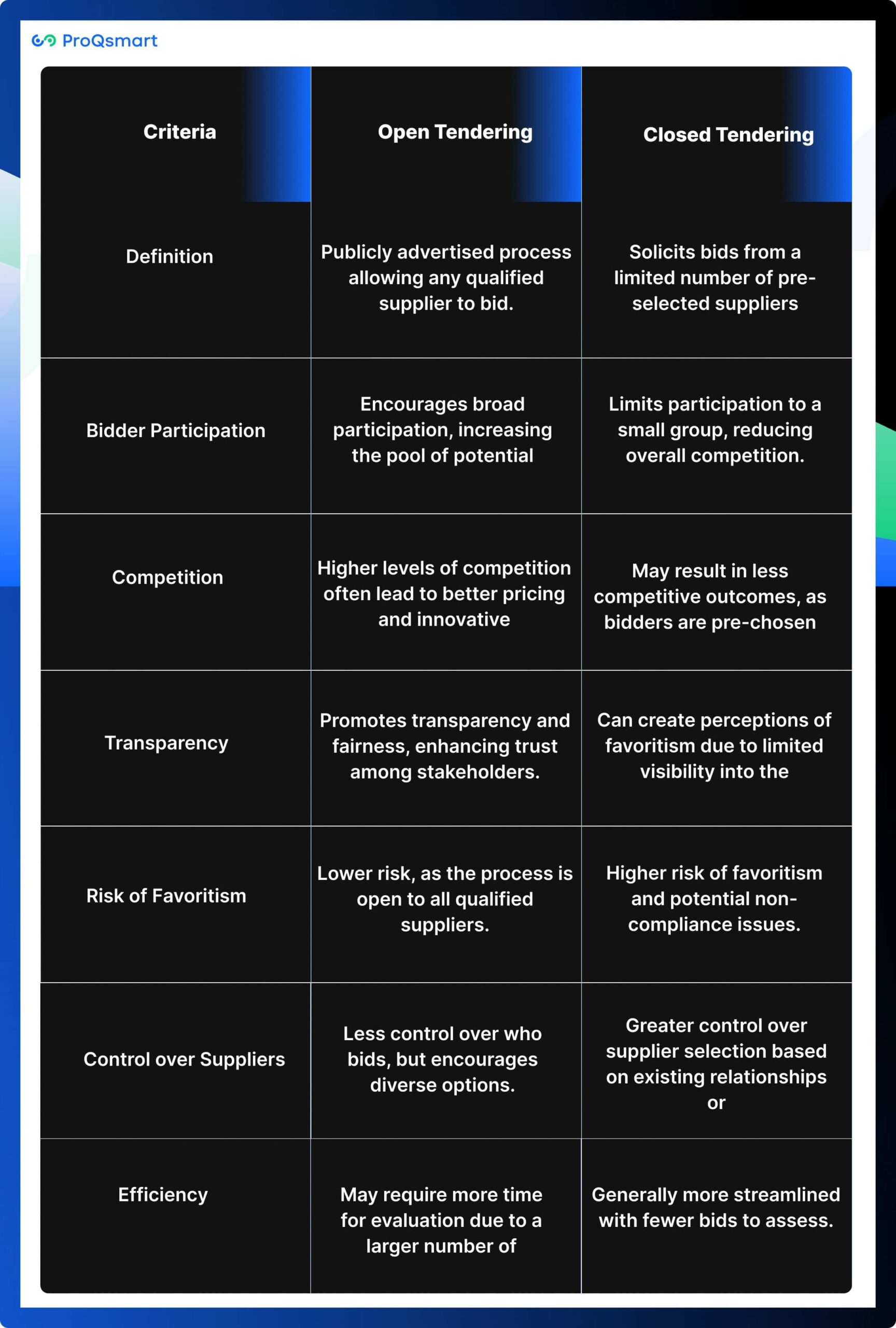
Criteria | Open Tendering | Closed Tendering |
Definition | Publicly advertised process allowing any qualified supplier to bid. | Solicits bids from a limited number of pre-selected suppliers. |
Bidder Participation | Encourages broad participation, increasing the pool of potential bidders. | Limits participation to a small group, reducing overall competition. |
Competition | Higher levels of competition often lead to better pricing and innovative solutions. | May result in less competitive outcomes, as bidders are pre-chosen. |
Transparency | Promotes transparency and fairness, enhancing trust among stakeholders. | Can create perceptions of favoritism due to limited visibility into the selection process. |
Risk of Favoritism | Lower risk, as the process is open to all qualified suppliers. | Higher risk of favoritism and potential non-compliance issues. |
Control over Suppliers | Less control over who bids, but encourages diverse options. | Greater control over supplier selection based on existing relationships or criteria. |
Efficiency | May require more time for evaluation due to a larger number of bids. | Generally more streamlined with fewer bids to assess. |
Scenarios Where Each Method Is Suitable
The choice between open and closed tendering largely depends on the specific needs of a project. Open tendering is particularly suitable for projects that prioritize transparency, fairness, cost-efficiency, and competition. This method is essential in public sector infrastructure projects, where accountability is critical. Open tendering encourages agencies to consider a wider range of suppliers, which can lead to increased competition and a greater likelihood of securing the best value.
On the other hand, closed tendering is more appropriate for complex and highly specialized projects. This method allows organizations to work with a select group of known and reliable suppliers, which can reduce risk and enhance quality. Closed tenders are often effective for niche requirements where specific expertise or proprietary technology is necessary. While this approach may limit competition, it provides the benefit of working with established vendors who understand the project’s unique needs.
Ultimately, matching the tendering method to the desired procurement outcomes is essential for achieving successful results. Additionally, e-tendering offers a modern alternative that combines the benefits of both methods while enhancing efficiency and accessibility. Utilizing platforms such as ProQsmart designed for e-tendering can streamline the process, making it easier to manage bids and communications effectively.
Other Types of Tendering Methods
In addition to open and closed tendering, several other procurement methods cater to specific project needs and requirements. Understanding these methods can help organizations choose the most appropriate approach for their procurement activities.
Two-Stage Tendering
This method consists of two distinct phases. In the first stage, suppliers submit technical proposals that outline their capabilities, methodologies, and solutions without including pricing information. After evaluating these submissions, the organization shortlists bidders who meet the required criteria and invites them to submit detailed financial proposals in the second stage. This approach is advantageous for projects with high complexity or uncertainty, as it allows organizations to assess technical competence before discussing costs, reducing the risk of selecting an unsuitable supplier.
Selective Tendering
Also known as restricted tendering, this method involves inviting bids from a pre-qualified list of suppliers who have demonstrated their capabilities and reliability in previous engagements. By limiting participation to capable vendors, organizations can ensure that they receive bids from suppliers who meet specific criteria related to quality, experience, or technical expertise. While this approach may reduce the pool of bidders, it helps maintain a level of competition among qualified suppliers.
Restricted Tendering
This method limits the invitation to tender to a select group of suppliers who have been pre-qualified based on their capabilities and past performance. By inviting only those suppliers who meet specific criteria, organizations can ensure that they receive bids from capable vendors while maintaining a level of competition. This approach can save time and resources in evaluating bids but may reduce the overall competitiveness of the process.
E-Tendering: For a Better Procurement Process
While traditional tendering methods have their advantages, e-tendering stands out as a superior alternative that enhances efficiency and accessibility across all procurement processes. E-tendering platforms streamline operations by digitizing documentation and enabling real-time communication between buyers and suppliers. This digital transformation reduces paperwork, minimizes errors, and accelerates decision-making.
Using an e-tendering platform like ProQsmart can significantly improve your procurement strategy by offering features such as automated document management, vendor performance tracking, and enhanced collaboration among stakeholders. By adopting e-tendering, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, cost savings, and improved outcomes in their procurement activities while ensuring transparency and fairness throughout the process.
Conclusion
Open tendering emphasizes the importance of fair competition and improved supplier choices, creating a level playing field for businesses of all sizes. While it offers numerous advantages, such as transparency and cost savings, it also faces challenges like longer timelines and the complexities of bid management. However, with careful planning and adherence to best practices—such as establishing clear requirements, robust evaluation criteria, and transparent communication—organizations can mitigate these risks and streamline the procurement process.
Despite the benefits of open tendering, many organizations are increasingly turning to e-tendering as a more efficient alternative. E-tendering addresses many of the challenges associated with traditional methods by automating processes, reducing paperwork, and enhancing communication. This digital approach not only saves time but also improves transparency and fosters greater participation from a wider range of suppliers.
For those looking to enhance their procurement strategy, utilizing an e-tendering platform like ProQsmart can provide significant advantages. ProQsmart simplifies the e-tendering process, making it easier to manage bids and communications effectively. Book a demo today!