Procurement is a fundamental business function that involves the process of sourcing and acquiring goods and services needed for organizational operations. It goes beyond mere purchasing, encompassing a series of strategic activities designed to optimize costs, enhance efficiency, and contribute to the overall success of the business. This blog post delves into the intricacies of procurement, shedding light on its processes, significance, and best practices.
Understanding Procurement
It involves identifying company needs, sourcing goods and services, negotiating contracts, and managing supplier relationships. It’s a critical activity that impacts a company’s bottom line, operational capabilities, and strategic positioning. Effective procurement ensures that businesses acquire the necessary resources at the best possible cost, quality, and timing.
Learn Centralized Purchasing for US Businesses 2024
Key Elements of Procurement
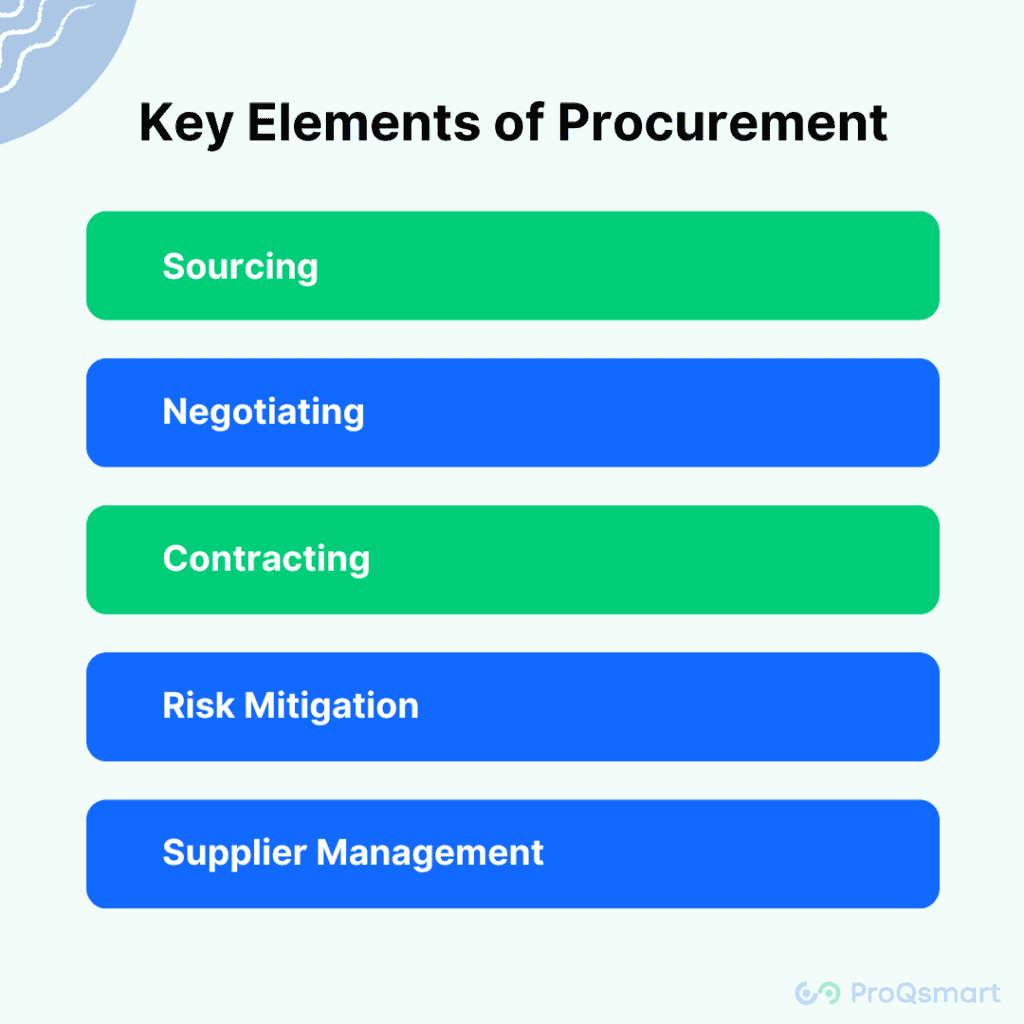
Sourcing
Identifying and evaluating potential suppliers to find the best fit for the company’s needs.
Negotiating
Working out terms and conditions with suppliers to achieve favourable agreements.
Contracting
Formalizing the purchase terms through contracts that specify pricing, delivery, and service-level agreements.
Purchasing
The actual buying of goods or services, often through purchase orders.
Supplier Management
Maintaining and enhancing relationships with suppliers to ensure ongoing value and performance.
The Strategic Role of Procurement
Procurement transcends transactional buying; it is a strategic function that influences the organization’s overall strategy. Strategic procurement involves:
- Aligning procurement activities with business goals.
- Managing risks in the supply chain.
- Fostering innovation through supplier collaborations.
- Achieving cost savings and efficiency gains.
Procurement Processes
The procurement process typically follows these steps:
Need Identification: Determining what goods or services are required.
Market Research and Supplier Evaluation: Investigating potential suppliers and evaluating their capabilities.
Tendering or Quoting: Requesting and comparing offers from suppliers.
Selection and Negotiation: Choosing the best supplier and negotiating terms.
Purchase and Order Management: Placing orders and managing the procurement cycle.
Delivery and Inspection: Receiving and inspecting the purchased goods or services.
Payment and Record Keeping: Completing financial transactions and maintaining records for future analysis.
Best Practices in Procurement
Leverage Technology: Utilize procurement software to streamline processes, improve accuracy, and gain insights into spending patterns.
Develop Strategic Supplier Relationships: Build strong partnerships with key suppliers to ensure reliability, quality, and innovation.
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider all costs associated with the lifecycle of a product or service, not just the purchase price.
Implement Sustainable Procurement: Prioritize environmental and social factors in decisions to support sustainability goals.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and optimizes the processes and strategies to adapt to changing market conditions and business needs.
Conclusion
Procurement is a vital aspect of business management, integral to sustaining operations, achieving financial goals, and driving strategic initiatives. By understanding and optimizing processes and embracing best practices, organizations can realize significant benefits, including cost savings, improved supplier performance, and enhanced market competitiveness. As businesses continue to evolve, the role of procurement buyer will increasingly become more strategic, underlining its importance in achieving long-term success.