The procurement process involves a structured approach to sourcing, selecting, and managing suppliers to meet organizational needs while ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Through rigorous strategic planning and cross-departmental collaboration, procurement professionals can help ensure that they’re driving economic value, strengthening supplier relationships, and mitigating operational risk. Leveraging modern tools and technology further streamlines workflows, enabling better decision-making and transparency.
As the green building movement continues to gain traction, unlocking the power of procurement will be key to making sustainable choices. From contract negotiations down to supplier performance evaluations, each action plays a role in fostering a strong supply chain.
An optimized procurement process means more than just cost savings. It ensures businesses are better prepared and more adaptable in the face of change.
What Is the Procurement Process?
Procurement is the process of obtaining and overseeing the provision of goods and services that are necessary for an organization to function. It’s fundamental to balancing costs with quality via competitive bidding and smart negotiations with suppliers. Sourcing raw materials for manufacturing is more than just considering costs.
You’ll need to judge the supplier’s capacity to deliver on time, since this has a direct effect on the efficiency of your production schedule. More than just cost, procurement improves the effectiveness of the supply chain through creating long-term, dependable relationships with suppliers.
This level of collaboration usually results in more favorable terms, expedited access to resources, and enhanced delivery timelines. Take, for instance, a construction company with deep relationships in place—they’re the ones who get the materials they need when demand is high.
Strategically, procurement helps to align purchasing decisions with a company’s broader goals and objectives. Procurement is an active partner to embed sustainability and community support into procurement processes. It uses sustainable practices and locally sources its materials to power these programs.
Overview of Procurement Steps
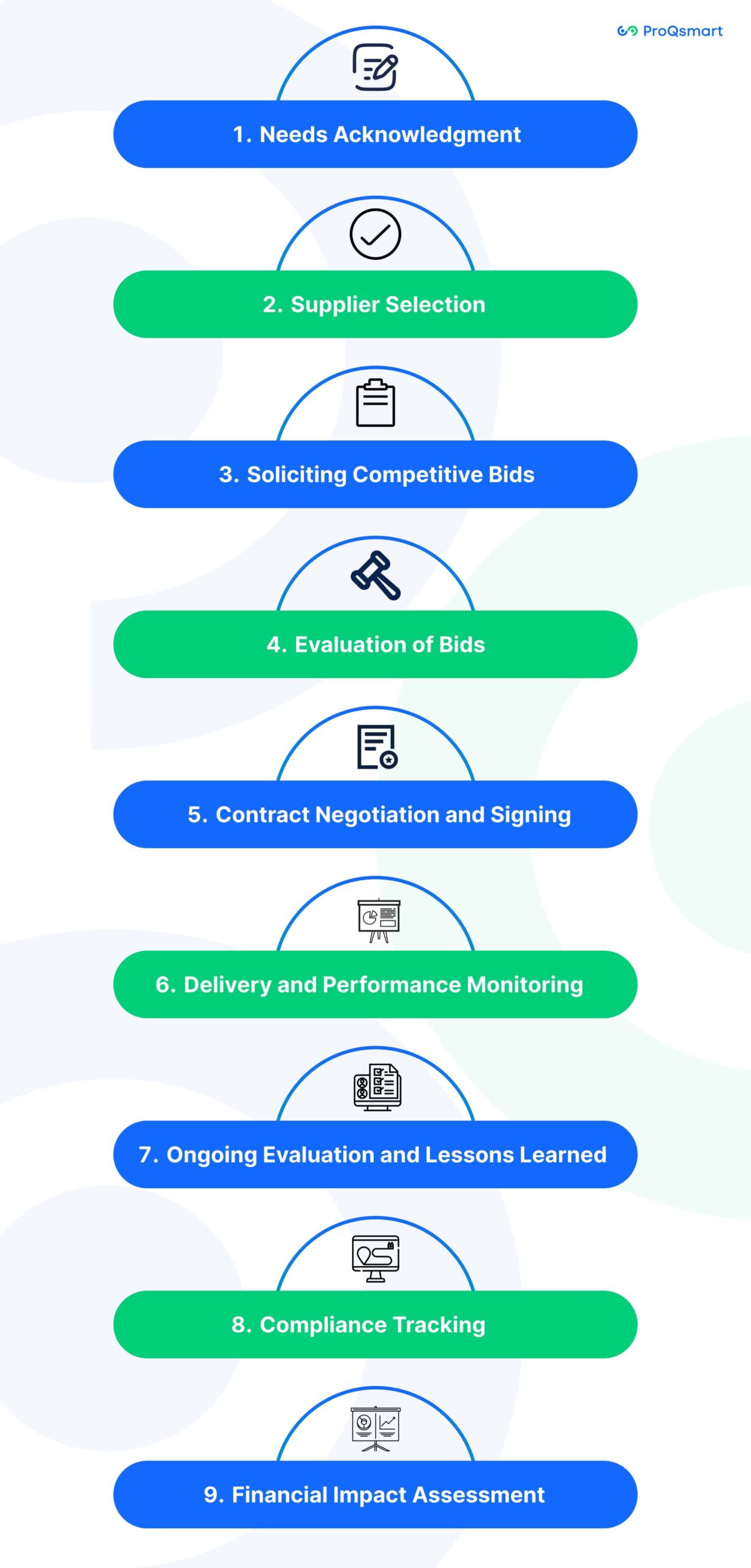
Needs Acknowledgment
The procurement process begins with recognizing and defining the specific needs of the organization. This initial step is crucial as it sets the foundation for the entire procurement journey
Supplier Selection
Following needs acknowledgment, the next phase involves selecting potential suppliers. This includes conducting market research to identify qualified vendors and gathering information on their capabilities.
Soliciting Competitive Bids
Once potential suppliers are identified, organizations solicit competitive bids. This step involves issuing requests for quotations (RFQs) or proposals (RFPs) to gather pricing and service offerings from various suppliers.
Evaluation of Bids
After receiving bids, organizations evaluate them based on criteria such as pricing, quality, technical expertise, and scalability. This evaluation helps in shortlisting the most suitable suppliers.
Contract Negotiation and Signing
Upon selecting a supplier, contracts are negotiated and signed. This includes establishing payment terms, pricing structures, and delivery requirements to ensure clarity and mutual agreement.
Delivery and Performance Monitoring
Following contract execution, the supplier delivers the goods or services as agreed. Organizations must monitor supplier performance to ensure compliance with contractual obligations and quality standards.
Ongoing Evaluation and Lessons Learned
After delivery, continuous evaluation of supplier performance is essential. Recording lessons learned from each procurement cycle helps improve future procurement strategies and processes.
Compliance Tracking
Ensuring compliance with regulations and internal policies is critical throughout the procurement process. This tracking helps maintain accountability and transparency in procurement activities.
Financial Impact Assessment
Finally, it’s important to assess the financial impact of procurement decisions. For nonprofits, procurement can control a significant portion of costs, making it vital for long-term financial sustainability.
How Procurement Process Impact in Business
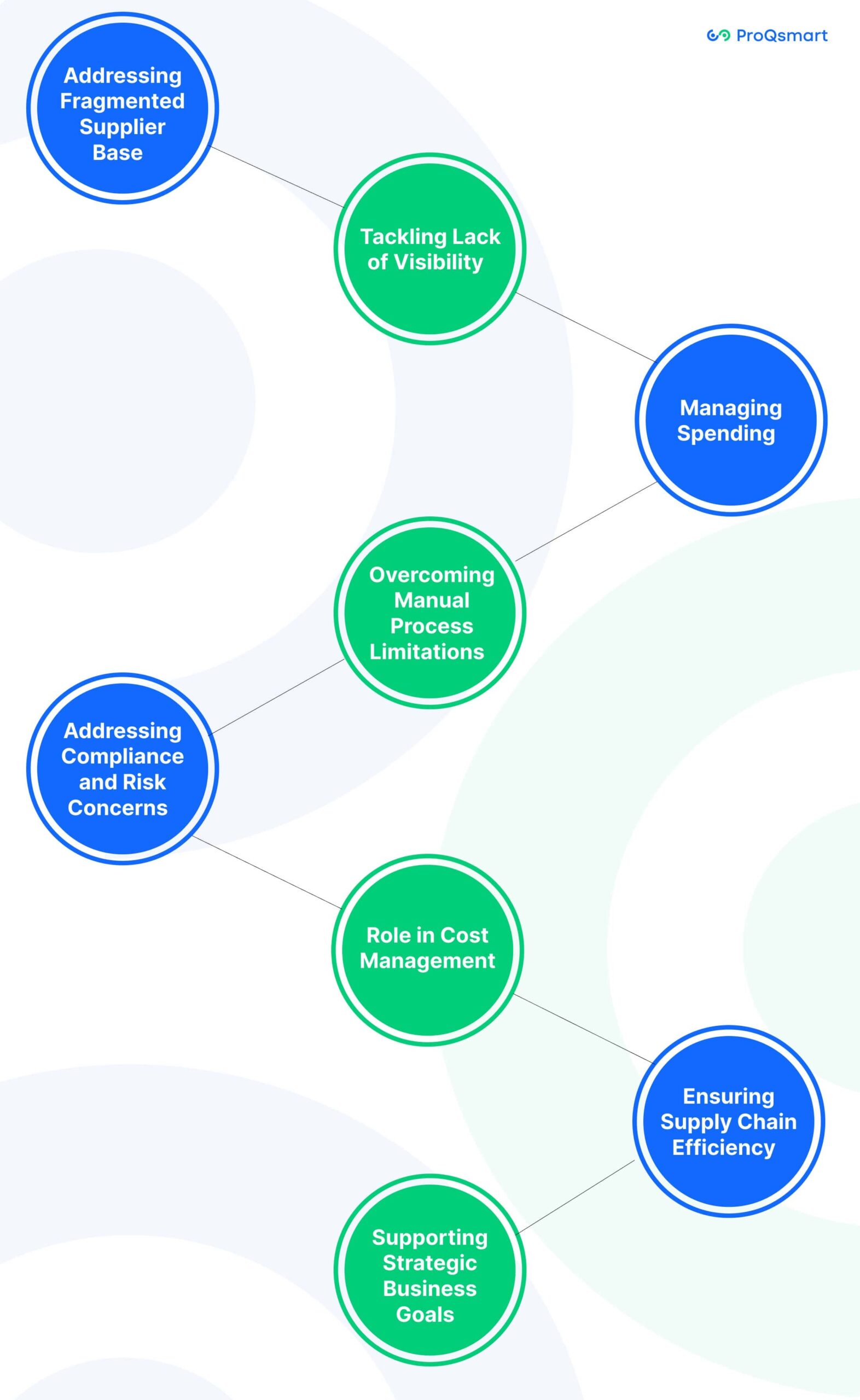
Addressing Fragmented Supplier Base
Inadequate visibility into a fragmented supplier base can result in management inefficiencies and higher costs. Consolidating suppliers makes it easier to oversee contractor work, avoid redundancies, and build meaningful relationships.
For example, a manufacturing company might decide to consolidate its suppliers from 50 down to 10. This transformation enables them to focus their efforts on suppliers that provide reliable quality and the best value.
This strategy not only makes operations smoother but increases negotiating leverage, leading to more favorable terms and long-term relationships.
Tackling Lack of Visibility
Procurement is usually challenged by a lack of visibility end-to-end, which creates challenges in tracking spend and measuring supplier performance. This technology challenge can be overcome with advanced tracking and reporting systems that provide managers with immediate access to detailed data.
As an example, adopting a solution that records purchase orders, delivery schedules, and vendor history provides a clear reporting picture. This transparency helps lawmakers make informed decisions and identify where they can save cash.
Managing Spending
Uncontrolled or unauthorized spending can throw budgets completely out of whack. Setting and enforcing procurement guidelines solves this problem by ensuring every purchase reflects company values.
Establishing a broad set of guidelines can help maintain uniformity in vendor selection and approval processes and help mitigate overspending. For instance, mandating pre-approvals for purchases above a certain dollar amount prevents overspending.
Overcoming Manual Process Limitations
Outdated, manual procurement methods are error-ridden and inefficient. Automating procurement using solutions such as e-procurement platforms speeds up processes and reduces errors.
Automated solutions have the ability to process purchase order generation and invoice matching automatically. For example, moving from manual paper-based processes to automated digital solutions leads to faster processing times by up to 60%.
Addressing Compliance and Risk Concerns
Ongoing policy review and supplier auditing are important measures for staying compliant and avoiding risk. By evaluating supplier practices, like ethical sourcing or adherence to regulations, companies protect their bottom line.
A large construction firm can easily ensure that suppliers are adhering to safety standards. This reduces potential liabilities and allows projects to run without unnecessary hitches.
Role in Cost Management
Procurement significantly impacts cost management, controlling as much as 40% to 80% of a company’s total expenses. Streamlining processes with technology reduces errors while improving efficiency.
Centralized procurement operations enhance coordination, while spend analysis identifies cost-saving opportunities. For example, conducting quarterly reviews of expenses can reveal redundant costs or opportunities for bulk pricing.
Strategic sourcing aligns procurement with business goals, and clear guidelines ensure consistent practices. Collaboration with stakeholders and regular supplier evaluations further optimize budgets.
Ensuring Supply Chain Efficiency
Efficient supply chains are based on well-established contract closure procedures that make sure obligations are fulfilled. Using a systematic supplier evaluation framework, companies can create a roadmap of supplier performance and areas for improvement.
Tools for data documentation help keep a clean and accurate procurement paper trail — an invaluable resource for any future audits or internal re-planning. Analyzing outcomes and supplier feedback to identify trends or inefficiencies allows you to dial-in on continuous improvement.
Supporting Strategic Business Goals
Procurement has, in turn, become a highly strategic function that fuels innovation and growth. Whether it’s your eProcurement tool like ProQsmart, mapping out each stage of the procurement process provides clarity, and tools that enhance visibility help ensure that you’re making informed decisions.
This transformation makes procurement a strategic player in accelerating operational excellence and enabling competitive advantage. After all, it directly influences organizational and budgetary success.
Key Stages of the Procurement Process
Recognizing Business Needs
The procurement process begins with identifying your business’s unique needs, which is crucial for effective procurement. Needs identification involves determining the items necessary to achieve operational or strategic goals. For instance, a traditional manufacturing company typically requires raw materials like steel or plastic, while a construction company often seeks services such as bulldozer or excavator rentals. Addressing these needs allows us to implement a streamlined procurement process that ensures we procure the right resources efficiently.
At this stage, teams have the opportunity to submit a purchase request. This request must clearly outline the quantity, quality, and delivery timeframes for the goods or services needed. A thorough procurement practice ensures that all specifications are met, leading to better outcomes.
It is essential to check the requisition package carefully. A completed requisition package is vital, as it must contain all required information before processing your request. This attention to detail helps avoid any missing information, which could hinder the procurement process flow.
By focusing on proper procurement and the corresponding solicitation process, businesses can enhance their procurement management process. This foundational step is instrumental in fostering strategic procurement efforts that contribute to overall procurement efficiency and cost control.
Soliciting and Engaging Suppliers
After determining those needs, the next step is discovering and engaging the right suppliers to meet requirements. This is where you begin the official procurement process by issuing requests for proposals (RFP), requests for quotes (RFQ), or tenders to prospective vendors.
Advanced procurement software like ProQsmart, which is increasingly being built into ERP systems, can automate this gatekeeping process. This accelerates the supplier review and selection process. For example, software can make bid evaluations faster, automatically compare suppliers’ responses, and provide a consistent, transparent process.
Evaluating Supplier Proposals
This step includes determining the best bid based on price, quality specifications, deliveries required, and vendor service record. This means it’s important to look for long-term value instead of just the lowest initial cost.
A three-way match process—matching the purchase order, invoice, and delivery receipt—provides an additional layer of supplier performance assurance.
Negotiating and Finalizing Contracts
The negotiation phase is where companies get on the same page regarding topics such as cost, timing of delivery, and consequences for breach of contract. Contracts should include detailed requirements regarding service levels, warranties, and dispute resolution to avoid the pitfalls of the past.
A smartly negotiated contract reduces all parties’ risks and lays the groundwork for positive supplier relationships.
Managing Orders and Deliveries
Once contracts are awarded, purchase order management and delivery tracking become key priorities. Procurement software can help you automatically create orders, track shipment progress, and flag delays.
For instance, automated notifications can warn teams when a delivery schedule is jeopardized, allowing for proactive changes to keep projects on track.
Approving Invoices and Payments
Ensuring that invoices are matched to purchase orders and delivery receipts is the payment process—a typical three-way match process. This final step double-checks for any discrepancies, preventing the possibility of overpayments or any other financial discrepancies.
Automation helps create more efficient approval workflows and can help accelerate payments—building confidence with suppliers.
Keeping Records and Documentation
Keeping clear and legible copies of supplier contracts, purchase orders, and proof of payment is important both for compliance and future audits. This documentation can be useful in evaluating procurement performance and informing future strategy development.
Procurement software like ProQsmart streamline record-keeping, making it more efficient and accessible.
Final Step in the Procurement Process
Closing Contracts with Suppliers
The last step starts with making sure all deals are kept. A careful examination of the contract language will hold suppliers accountable to deliver what they promise. That means providing the goods or services according to the specified quality standards and deadlines.
This is where the three-way matching process comes into play. By comparing the purchase order (PO), invoice, and receipt, any issues can be caught and fixed prior to payment approval. This secures not only the validity of the transaction but the transparency of each transaction.
For example, if the invoice shows more than what was actually received, the discrepancy can be quickly resolved. An efficient three-way matching tool saves time and reduces errors. Since manual processes can create further inefficiencies, strengthening the case for the need for this tool.
Evaluating Supplier Performance
Measuring supplier performance is critical to long-term success. This means tracking on-time delivery, quality of deliverables, and responsiveness. Whether by a scoring system or a feedback loop, it is fundamentally important to have transparency.
For instance, a supplier who is regularly late or providing subpar goods could be marked for performance review meetings or even future re-evaluation. This concerted evaluation process protects a stable supplier base.
Documenting Lessons Learned
Documenting lessons learned from each procurement cycle helps to create a cycle of continuous improvement. By bringing together and highlighting both successes and challenges, teams are able to focus their strategies better and missions.
For example, if one of your suppliers provided exceptional service, outlining their successful approach can help you work with them on future projects.
Managing Compliance and Risks
Ensuring adherence to both regulatory and organizational standards of practice is paramount. Strategic risk management must plan for risks such as late deliveries or violation of contracts.
A single, system-wide approach to compliance monitoring allows for fewer disruptions and mitigates liability.
Facilitating Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement only works with a collaborative spirit. Establishing a culture of ongoing process review and being open to feedback from the team promotes this efficiency.
Using technology to automate repetitive tasks is another way to improve workflow.
Common Challenges in Procurement
Fragmented Supplier Base Issues
A fragmented supplier base leads to inefficiencies, making it challenging for procurement teams to track supplier performance effectively.
This fragmentation can result in inconsistent pricing, delivery delays, and a lack of standardization in goods or services.
Domestic manufacturers sourcing from numerous small suppliers often face disruptions due to unpredictable supply chains.
Lack of Visibility in Processes
An opaque procurement process hinders informed decision-making and can lead to significant financial losses for organizations.
Inaccurate or outdated data exacerbates this issue, making it difficult to assess supplier credentials and increasing the risk of partnering with high-risk vendors.
Managing Undermined Spending
Maverick spending, or unauthorized purchases, undermines budgetary controls and contributes to procurement inefficiencies.
This rogue spending often arises from weak policy enforcement or lack of oversight.
Overcoming Manual Process Limitations
Clunky manual procurement processes are time-consuming and error-prone, limiting flexibility in responding to market opportunities.
These limitations can hinder the efficiency of procurement teams and slow down overall processes.
Addressing Compliance and Risk Concerns
- Compliance and risk management are critical components of procurement; without standardized approaches, organizations expose themselves to legal and reputational risks.
- Recognizing and evaluating risks such as supplier non-compliance or geopolitical tensions is essential for effective procurement management.
Strategies to Optimize the Procurement Process

Streamline Processes with Technology
Integrating technology into procurement simplifies operations and minimizes errors. Tools or procurement software such as ProQsmart, automate repetitive tasks, reducing manual data entry mistakes and saving time. ProQsmart can generate purchase orders or track invoices, freeing up your team’s capacity for strategic work.
Implementing technology enhances visibility into procurement activities, enabling better decision-making. By using automated systems, you can track spending patterns, evaluate supplier performance, and identify inefficiencies. This approach improves accuracy and ensures compliance with procurement policies.
Centralize Procurement Operations
Moving to a centralized procurement operation consolidates operations and moves all procurement activities under one umbrella. This strategy improves accountability and transparency among the entire procurement process.
For example, consolidating all supplier data into one platform allows you to track all transactions and spending patterns in one place and more easily identify issues. Centralized procurement further reduces requisition-to-payment cycles, expediting approvals and payment to vendors.
With a single system, companies save money by eliminating unnecessary duplicate purchases and avoiding maverick spending.
Conduct Regular Spend Analysis
Spend analysis is a foundational element of an optimized procurement process. Scrutinizing expenditures finds opportunities to save and exposes wasteful inefficiencies. Start with the top 20-50 suppliers, so you can get a better idea of where most of your budget is being spent.
If a supplier’s costs increase with no value add, push back. Spend analysis isn’t just a cost-saving measure, either. It aligns with sustainability goals by helping organizations identify where they can implement more sustainable practices.
Implement Strategic Sourcing Methods
Unlike strategic sourcing, which focuses on long-term value rather than short-term wins, it’s about finding the best suppliers that fit within your overall business objectives – whether it’s cost, quality, or sustainability.
For instance, working with suppliers that align with your efforts to minimize environmental harm can help boost your brand’s reputation. In addition to optimizing financial impact, strategic sourcing helps manage risk by building relationships with trustworthy, prequalified suppliers.
Establish Clear Procurement Guidelines
Having clear, publicly available guidelines helps make sure that procurement practices are uniform and streamlined. That means creating clear approval workflows, determining spending limits, and detailing criteria for vendor selection.
For instance, a regulation that mandates three competitive bids for purchases over $5,000 encourages fairness and cost-effectiveness. Having everything documented in written policies means less confusion and quicker onboarding for new staff, so your work can continue uninterrupted.
Foster Collaboration with Stakeholders
Asking stakeholders to weigh in on procurement decisions fosters an alignment between short- and long-term organizational goals and procurement strategies. Consistent collaboration with key departments such as finance, operations, and legal helps to make sure that procurement is aligned with the organization’s larger business goals.
For instance, engaging early and often with the finance team ensures that budgets are closely followed with procurement plans and overspending is avoided. Working together not only builds trust and relationships, it breeds innovation, with different perspectives leading to creative solutions.
Monitor and Improve Supplier Relationships
Fostering good relations with suppliers is essential to procurement. Clear expectations and accountability, regular performance reviews, and an open line of communication develop trust and ensure each party’s continued growth.
For example, providing feedback on delivery timelines or product quality allows suppliers to provide better service to the organizations. Developing targeted strategic partnerships with trusted vendors lowers risk and loss potential while building your organization’s reputation as a strong partner.
Additional due diligence, such as tracking the financial health of your vendors, adds another layer of security to your supply chain.
Best Practices for Managing the Final Step
Set Clear Contract Closure Procedures
Adopting a clear and consistent process of contract closure makes sure all commitments are wrapped up neatly. Start with ensuring that the three-way matching process—matching up the purchase order, invoice, and receiving report—is finalized. When you complete the verification of the invoice, approve it immediately.
Next, take the payment through in accordance with the terms specified in the contract and/or purchase order. This final step prevents confusion by sticking to established, in-writing payment terms. Contract management AI tools such as ProQsmart can help review contracts faster by analyzing clause to clause, making sure you are compliant and lowering any risk you may have.
Create a Supplier Evaluation Framework
Supplier performance evaluation at the end of the procurement cycle is critical. Create a performance framework that includes delivery speed, accuracy of goods delivered, price accuracy, and communication. For instance, monitoring a supplier’s historical performance on meeting deadlines can surface patterns of reliability.
When you use a centralized platform, such as an ERP system or a procurement-specific tool like ProQsmart, monitoring performance is a breeze. You can easily identify shifting trends and take data-driven action.
Use Tools for Data Documentation
Centralized documentation is critical for tracking and improving procurement processes over time. Technology such as ERP systems provide a centralized repository for contract data, payment data, and supplier performance information.
This streamlining allows for increased oversight, more informed negotiation of future agreements, and identification of areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Mastering the procurement process not only enhances efficiency and generates significant savings but also fosters lasting relationships with suppliers. By setting realistic objectives and employing innovative strategies, even the most challenging steps become manageable. Identifying potential obstacles early on allows organizations to avoid delays and maintain smooth operations. Adopting best practices not only creates a level playing field but also minimizes the risk of fraud.
Effective procurement practices are integral to business growth, opening avenues for cost reduction, quality improvement, and environmentally sustainable initiatives. Whether refining vendor selection or enhancing contract management, each advancement contributes to long-term value creation.
To start improving your procurement process today, stay informed about industry trends, invest in the right tools, and be ready to adapt as market conditions change. Implementing a strategic public procurement approach now will lay a solid foundation for your organization’s future success. For those looking to streamline their procurement efforts further, consider exploring ProQsmart. This platform can help optimize your processes and drive efficiency. Book a demo today to see how ProQsmart can transform your procurement strategy and set your business up for success tomorrow.